农作物秸秆是农业生产中主要的产物之一,也是主要的农业废弃物,其含有丰富的氮、磷、钾大量元素以及中微量元素,同时含有纤维素、半纤维素、木质素、蛋白质和糖类等有机能源[1]。在农业生产过程中,秸秆是一种重要的生物质资源,秸秆还田作为一种保护性耕作措施,能培肥土壤[2]、降低土壤容重[3]、改善土壤结构[3–4]、增加土壤养分速效量[5]、促进作物增产[6],还可通过增加土壤有机碳的直接输入实现固碳,维持土壤有机质平衡[7],促进土壤养分循环,同时秸秆还田与化肥配施可以减少10%~20%氮、磷、钾化肥用量[8]。王振忠等[9]研究表明,与单施化肥处理相比,秸秆与化肥配施土壤生产力提高了19.5%,当季氮肥利用率提高了13.2%,稻、麦分别增产6.2%和3.7%。秸秆配施氮磷钾肥同时可减少土壤养分流失,徐泰平等[10]研究了冬小麦-夏玉米轮作区秸秆还田对紫色土坡耕地养分流失的影响,结果表明,与单施化肥相比,氮磷钾肥与秸秆配施能减少泥沙量和地表径流量,增加渗漏径流量,并显著减少氮、磷的流失,减幅达到60%~76%。研究认为,秸秆还田的持续时间越长,越能体现其对土壤理化性状的改善作用[11]。
中国具有丰富的生物质资源,农业每年产生各类农作物秸秆约为7亿t,其中水稻、小麦和玉米等大宗农作物秸秆在5亿t左右[12]。由于缺乏切实可行的处理与利用技术,每年焚烧掉的秸秆超过2亿t,其损失的氮、磷、钾相当于全国化肥总产量的 60%左右[13]。这不仅造成秸秆资源的巨大浪费,还导致了严重的环境污染[14–15]。而秸秆资源数量的估算是秸秆资源能够综合利用的基础。已有学者采用不同的方法对其进行研究,方放等[16]研究得出2012年京津冀地区农作物秸秆资源总产量为5406.9 万t,秸秆中氮、磷、钾养分资源总量分别达到3.7万t、7.4万t、1.0万t。包建财等[17]估算了2009年西部七省区 (甘肃、新疆、内蒙古、青海、宁夏、陕西和西藏) 农作物秸秆资源理论数量达到0.882亿t,秸秆养分资源量为237万t,其中氮、磷和钾三种养分的总量分别为86.3万t、26.5万t和124万t。戴志刚等[18]估算了2009年全国主要农作物秸秆产量约6.64亿t,折合纯N 600.80万t、P2O5 92.56万t、K2O 940.86万t。可见,我国不但秸秆资源丰富,而且氮磷钾养分资源数量巨大。
虽然我国对秸秆资源相关研究较多,但多数学者是对秸秆利用状况的研究[19–23],并且大多集中在区域尺度[16, 22–24],或者单一的某种、某类作物[20, 22, 25–27]。在国家尺度上对秸秆资源的分析鲜有报道,而且秸秆养分资源数量对化肥减施的影响未见研究。因此,本文利用2016年国家统计数据和对已发表资料的统计,探讨和分析了中国秸秆资源数量及其养分资源量,以期为中国秸秆资源的高效利用提供理论依据。
1 研究方法与数据来源 1.1 研究对象与区域划分本文主要研究对象为中国大陆31个省、市、自治区,不包括香港、澳门、台湾和南海群岛。将中国分为六大农区[28]:东北地区,包括黑龙江、吉林和辽宁 3省;华北地区,包括北京、天津、河北、河南、山东、山西6省 (市);长江中下游地区,包括上海、江苏、浙江、安徽、湖北、湖南、江西 7 省 (市);西北地区,包括内蒙古、陕西、宁夏、甘肃、青海、新疆 6 省 (自治区);西南地区,包括重庆、四川、贵州、云南、西藏 5 省 (市、自治区);东南地区,包括福建、广东、广西、海南 4 省 (自治区)。研究的作物有水稻、小麦、玉米、大豆、马铃薯、花生和油菜。
1.2 种植制度划分根据相关研究资料[29–31]和2015年各种作物种植面积,将中国划分为双季稻种植区,包括海南、广西、广东、福建、江西、湖南和浙江7省 (自治区);稻麦轮作区包括上海、安徽、湖北和江苏4个省 (市);小麦玉米轮作区包括河南、山东、山西、河北、天津、北京、陕西、宁夏、甘肃和新疆10个省 (市、自治区);水稻/玉米单作区包括重庆、四川、贵州、云南、辽宁、吉林和黑龙江7个省 (市);小麦单作区包括青海和西藏2个省 (自治区);玉米单作区为内蒙古自治区。
1.3 秸秆养分资源数量核算方法中国历史上对作物秸秆养分资源产量没有专门的统计,本文参考国际上比较通用的和大多数研究所采用的方法,即通过作物经济产量与秸秆资源数量的关系 (草谷比) 计算得到秸秆产量 (Wj),根据其养分含量计算养分资源量。计算公式如下:
| ${{W}}i = \mathop \sum \limits_{j = 1}^7 Yij \times Rj \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad$ |
| ${W{\rm N}}\left({\rm{N}} \right) = {{Wj}} \times {{N}}j\quad\quad\quad\quad\,\,\,$ |
| ${W{\rm P}}\left({{{\rm{P}}_2}{{\rm{O}}_5}} \right) = {{Wj}} \times {{P}}j \times 2.29\,\,$ |
| ${W{\rm K}}\left({{{\rm{K}}_2}{\rm{O}}} \right) = {{Wj}} \times {{K}}j \times 1.2\,\,\,\,\,$ |
式中:Wi—第i个省市自治区农作物秸秆资源数量;Yij—第i个省市自治区的第j种农作物的产量;Rj—第j种农作物的草谷比;WN—秸秆氮素 (N) 养分资源量;Wj—第j种农作物秸秆资源数量;Nj—第j种农作物秸秆氮素养分含量;WP—秸秆磷素 (P2O5) 养分资源量;Pj—第j种农作物秸秆磷素养分含量;2.29—单质磷折算为五氧化二磷 (P2O5) 的系数;WK—秸秆钾素 (K2O) 养分资源量;Kj—第j种农作物秸秆钾素养分含量;1.2—单质钾折算为氧化钾 (K2O) 的系数。i=1, 2, 3, ……, 31,j=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6。
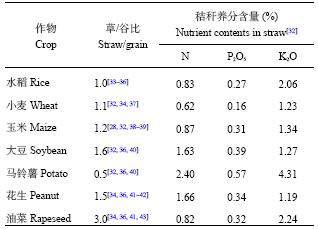
本文涉及的农作物产量和种植面积均来自于《中国统计年鉴2016》和《中国农村统计年鉴2016》。农作物秸秆数量计算中的草谷比通过国内外大量相关文献收集和整理所得,秸秆中氮磷钾养分含量参照全国农业技术推广服务中心数据 (表1)[32]。
| 表1 不同作物的草谷比和秸秆养分含量(风干基) Table 1 The ratio of grain to straw and the nutrient contents in straws (air-dried base) |
 |
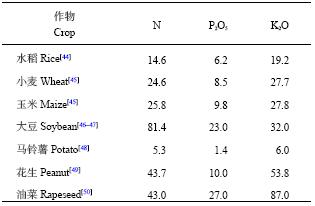
不同作物生长所需化学养分量是根据不同作物养分需求系数与产量乘积所得 (表2)。
| 表2 作物单位经济产量所需吸收的养分数量 (kg/t) Table 2 Nutrient requirement for unit economic yields of different crops |
 |
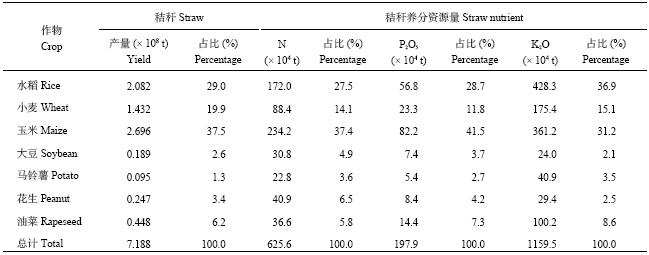
本研究估算2015年中国主要农作物秸秆资源量为71878.53万t (表3),其中秸秆数量仍以水稻、小麦和玉米三大粮食作物最大,分别占到总量的29.0% (水稻)、19.9% (小麦) 和37.5% (玉米),其他作物秸秆资源量仅占13.6%。从秸秆养分资源量看,三大粮食作物养分资源数量分别占总养分量的33.1% (水稻)、14.5% (小麦) 和34.2% (玉米),其他作物以油菜秸秆养分数量最高,占7.6%。秸秆养分总量中钾养分数量最高,其次分别为氮和磷,分别占总养分量的58.5% (K2O)、31.5% (N) 和10.0% (P2O5)。作物秸秆养分数量中以玉米氮和磷养分数量最高,分别占单质养分总量的37.4% (N) 和41.5% (P2O5);钾养分数量以水稻最高,占36.9% (K2O)。
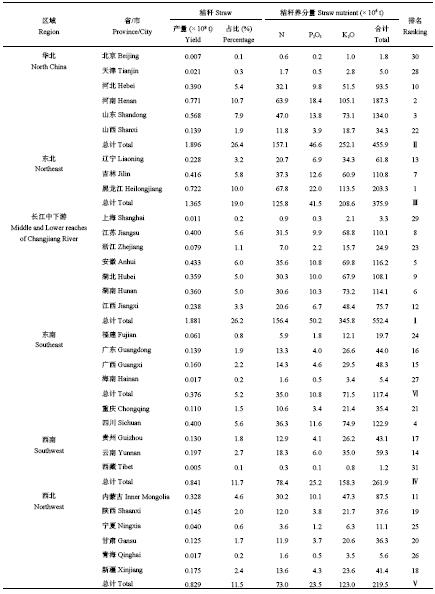
2.2 主要农作物秸秆资源分布从不同地区秸秆及其养分资源分布来看,2015年中国31个省市自治区的秸秆及其养分资源分布各地区差异较大 (表4),华北和长江中下游地区秸秆总量较多,分别占全国总量的26.4%和26.2%,其中秸秆数量前3的省份是河南、黑龙江和山东,分别占全国秸秆总量的10.7%、10.0%和7.9%。秸秆养分资源总量最高的为黑龙江省,其次为河南和山东,分别占全国秸秆养分资源总量的10.3%、9.5%和6.8%。从各省的秸秆数量看,大于3000万t的省 (市、自治区) 11个,2000万t~3000万t的省 (市、自治区) 2个,1000万t~2000万t的省 (市、自治区) 9个,100万t~1000万t的省 (市、自治区) 7个,低于100万t的省 (市、自治区) 仅2个。
| 表3 2015年中国不同作物秸秆所含养分资源量及其在全部秸秆中的占比 Table 3 Crop straw yield, contained nutrient quantities and their percentages in the whole straw yileds in China in 2015 |
 |
| 表4 2015年中国不同地区秸秆养分资源分布 Table 4 Distribution of straw nutrient resources in different regions of China in 2015 |
 |
中国2015年主要农作物产量为6.3亿t,包括水稻、小麦、玉米、大豆、马铃薯、花生和油菜,种植面积1.2亿hm2,作物理论N、P2O5和K2O需求量分别为1500万t、600万t、1700万t,需求比例为1∶0.4∶1.2(N∶P2O5∶K2O)(表5)。在生产中三大粮食作物仍占据主要地位,其中作物产量和种植面积以玉米最高,其次为水稻和小麦,而对N、P2O5和K2O需求量玉米远高于其他作物,其需求量分别占总量的40.1% (N)、40.3% (P2O5) 和37.8% (K2O),小麦对氮的需求量略高于水稻,水稻对P2O5和K2O的需求量高于小麦。在本研究的作物中产量和种植面积最低的分别为大豆和花生,马铃薯对N、P2O5和K2O需求量最低,其次为花生和大豆。
| 表5 2015年中国主要作物产量、种植面积及养分需求量 Table 5 Yields, area and nutrient requirement of major crops of China in 2015 |
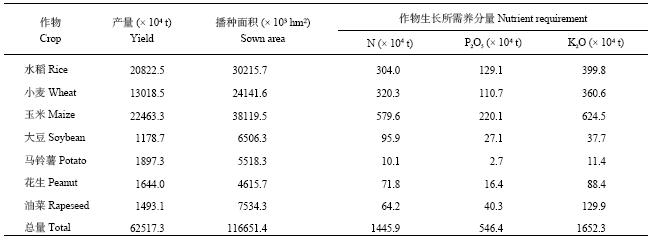 |
秸秆作为农业生产中重要的副产物,含有丰富的养分。由表6可以看出,若将秸秆全量还田平均相当于N 54.4 kg/hm2、P2O515.5 kg/hm2和K2O 88.1 kg/hm2施入农田土壤中,其中三大粮食作物 (水稻、小麦和玉米) 秸秆全量还田其N、P2O5、K2O施入量分别为56.9、18.8和141.8 kg/hm2 (水稻),36.6、9.7和72.7 kg/hm2 (小麦),61.5、21.6和94.8 kg/hm2 (玉米),本研究的主要农作物秸秆中分别以花生秸秆中氮,玉米秸秆中磷和水稻秸秆中钾养分量最高。从目前研究的不同作物最佳施肥量看,N、P2O5和K2O平均施用量分别为157.3、83.2和107.3 kg/hm2,施用比例为1∶0.5∶0.7 (N∶P2O5∶K2O)。
| 表6 不同作物秸秆养分量和最佳施肥量(kg/hm2) Table 6 The amounts of straw nutrients and optimum fertilizer rates |
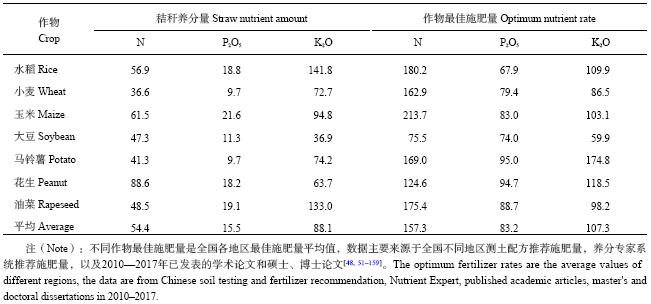 |
按目前研究的不同作物最佳施肥量计算,秸秆全量还田N、P2O5、K2O输入量平均分别占化肥用量的38.4% (N)、18.9% (P2O5) 和85.5% (K2O)(表7)。三大粮食作物 (水稻、小麦和玉米) 对氮肥需求量最大,秸秆全部还田氮的输入量分别占其化肥氮施用量的31.6% (水稻)、22.5% (小麦) 和28.8% (玉米);大豆和花生作为固氮作物,其每公顷秸秆中氮的数量占化肥施用量的62.6% (大豆) 和71.1% (花生)。分析秸秆中养分磷发现,其养分还田占化肥施用量百分比不同作物之间变化较小,其百分比介于10.2%~27.7%之间。而秸秆还田钾的输入量较高,其中2/3油菜秸秆还田钾的输入与其化肥钾的用量相近,水稻、小麦和玉米秸秆全量还田钾的输入量分别占相应化肥用量的129.0%、84.0%和91.9%。
| 表7 不同比例的秸秆还田带来的养分可替代化肥养分施用量的百分比 (%) Table 7 Percentage of chemical nutrients substituted by the straw nutrient from different straw returning ratio |
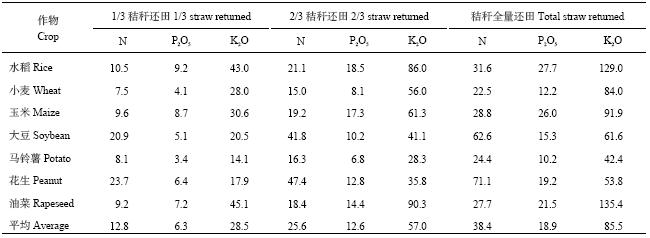 |
从不同种植制度下不同地区秸秆养分量分布来看,同一作物秸秆同一养分量差异较大 (表8),水稻秸秆中氮和钾均以长江中下游地区稻麦轮作制度下最高 (N 69.1 kg/hm2、K2O 172.0 kg/hm2),最低是东南地区双季稻中的晚稻 (N 45.1 kg/hm2、K2O 112.3 kg/hm2);小麦秸秆中氮和钾均以华北地区小麦玉米轮作制度下最高,西北地区小麦玉米轮作制度下最低,平均高出49.2%;玉米秸秆中氮和钾均以东北地区水稻和玉米单作制度下最高,西南地区水稻和玉米单作制度下最低,平均高出27.6%。从研究的不同作物最佳施肥量看,氮肥施用量以玉米最高,其次为小麦;磷肥施用量以小麦最高,其次为玉米;钾肥施用量以水稻最高,其次为玉米。
| 表8 不同种植制度下作物最佳施肥量及秸秆养分资源量 (kg/hm2) Table 8 Optimum fertilizer rates and straw nutrient under different cropping systems |
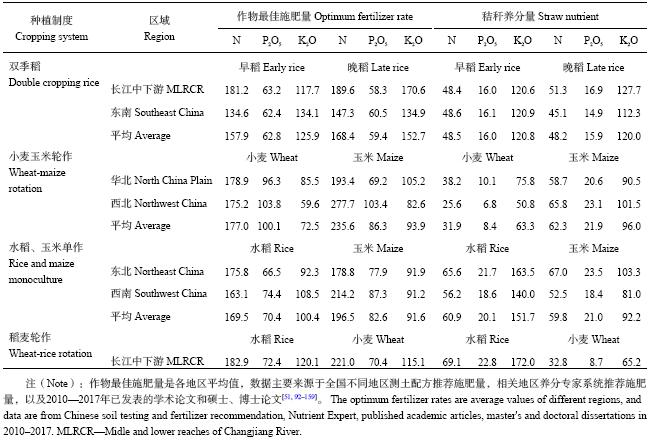 |
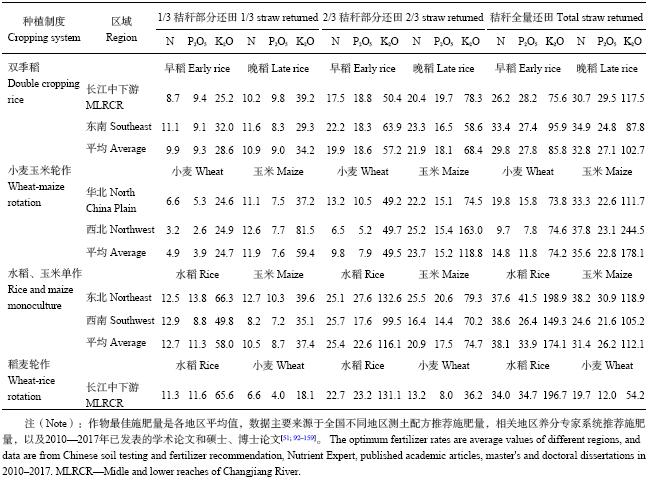
秸秆还田是秸秆资源综合利用的主要形式,同时也是减少作物施肥量的重要途径。由表9可以看出,理论上在双季稻种植区,早稻秸秆全量还田平均可以替代晚稻29.8% (N)、27.8% (P2O5) 和85.8% (K2O) 的化学养分施用量,晚稻秸秆全量还田平均可以替代早稻32.8% (N)、27.1% (P2O5) 和102.7% (K2O) 的化学养分施用量。在冬小麦夏玉米轮作区,小麦秸秆全量还田平均可以替代夏玉米14.8% (N)、11.8% (P2O5) 和74.2% (K2O) 的化学养分施用量,夏玉米2/3秸秆还田基本完全替代冬小麦化肥钾的施用量,全量还田可以替代35.6% (N) 和22.8% (P2O5) 冬小麦化学养分施用量。在水稻、玉米单作区,水稻2/3秸秆还田基本完全替代下季水稻化肥钾的施用量,全量还田可以替代38.1% (N) 和33.9% (P2O5) 下季水稻化学养分施用量,玉米秸秆全量还田可以替代31.4% (N) 和26.2% (P2O5) 下季玉米化学养分施用量,完全替代化学钾施用量。在稻麦轮作区,水稻2/3秸秆还田可完全替代小麦化肥钾的施用量,全量还田可以替代34.0% (N) 和34.7% (P2O5) 小麦化学养分施用量,小麦秸秆全量还田可以替代水稻19.7% (N)、12.0% (P2O5) 和54.2% (K2O) 的化学养分施用量。
| 表9 秸秆不同还田比例替代下季作物化肥施用量百分比 (%) Table 9 Percentage of straw nutrients for returning to field substituted for chemical fertilizers in next crops |
 |
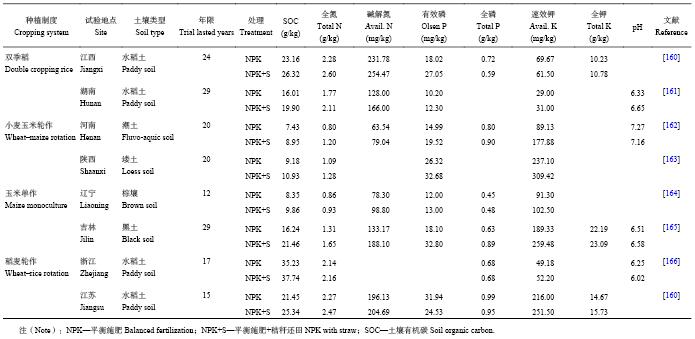
长期不同养分管理研究对土壤质量提升和维持其可持续生产力有重要理论意义。本研究收集了部分地区已公开发表的长期定位试验结果 (> 10年,表10),结果发现,不同耕作制度下长期秸秆还田均可增加土壤中有机碳、全氮、碱解氮和全钾含量,其含量NPK+S处理较NPK平均增加19.1% (SOC)、18.1% (TN)、22.6% (AN) 和5.6% (TK),部分地区长期定位试验结果NPK+S处理土壤有效磷、全磷、速效钾和土壤pH低于NPK处理,但其平均含量NPK+S处理高于NPK处理,分别高出27.4% (AP)、6.4% (TP)、24.6% (AK) 和0.2% (pH)。因此,长期秸秆与化肥的配合施用对土壤养分含量提高和质量改善均有积极作用。
| 表10 长期秸秆还田对土壤肥力的影响 Table 10 Effects of long-term straw return on soil fertility |
 |
中国作为农业大国,随着农业综合生产水平的持续提高,秸秆总产量总体呈不断增长趋势,1990年中国秸秆总产量不到7亿t [39],到2000年农作物秸秆总产量达7.5亿t [167]。已有研究对中国各年份秸秆资源数量进行了估算,但结果存在一定的偏差。毕于运等[39]研究认为2005年中国秸秆资源总量估算为8.41亿t,谢光辉等[168]估算为8.42亿t,王亚静等[169]认为是6.86亿t,曹国良等[170]估算中国2005年主要农作物秸秆量为6亿t,朱建春等[171]通过估算认为是6.34亿t,汪海波等[172]计算所得的结果为7.45亿t,张培栋等[33]的研究结果为 7.29亿t;高利伟等[36]估算得出2006年全国秸秆资源总量为7.62亿t,朱建春等[171]估算为6.52亿t,崔明等[173]的研究结果为4.33亿t,谢光辉等[174]的估算结果为6.54亿t,朱建春等[171]估算结果为秸秆总量达6.98亿t;王舒娟等[175]估算2012年我国秸秆理论资源总量为8.63亿t;本研究估算2015年中国主要农作物秸秆资源量为7.19亿t。结果的差异主要由于不同研究者获取统计数据来源有差异,对作物秸秆的界定不一致导致研究对象或范围不一致,以及秸秆系数的选取问题均导致了结果的差异[172],同时受作物生长环境、播种面积、估算精度等因素的影响,中国秸秆资源量估算结果同样存在年际差异和年内差异[21]。虽然这些研究结果存在一定差异,但均证明了中国农作物秸秆资源量巨大,具有很大的利用潜力。若需准确系统地获得可比性较强的估算结果,应对不同地区秸秆系数和养分含量进行测定分析,然后通过科学统一的估算方法得到中国秸秆资源量的最佳估算值。
农作物秸秆是农业生产中主要的产物之一,也是主要的农业废弃物,其含有丰富的氮、磷、钾大量元素以及中微量元素[1],对其进行肥料化、能源化和饲料化等一系列资源化利用,在促进农业的可持续发展和维护生态平衡方面起到重要作用。高祥照等[176]估算2000年中国秸秆资源总量达5.54亿t,其中含N、P2O5、K2O分别为493.9万t、156.7万t、982.5万t,总养分为1633.2万t;戴志刚等[18]对2009年全国农作物秸秆总产量的估算值为6.46亿t,其中N 600.80万t、P2O5 92.56万t、K2O 940.86万t;本研究估算2015年中国主要农作物秸秆的N、P2O5、K2O养分资源总量分别达到625.6万t、197.9万t、1159.5万t。各年的气候条件的差异,作物的生物产量和养分吸收量会存在差别,秸秆养分资源量也会不同,以及随着施肥措施日益完善,作物对养分的奢侈吸收,生产技术条件的进步,更多的秸秆资源可能被收集,秸秆养分资源量可能随之增加[21]。因此,秸秆养分资源量的利用不但可以降低环境污染,同时能够实现农田化肥减施,提高秸秆养分资源利用率。
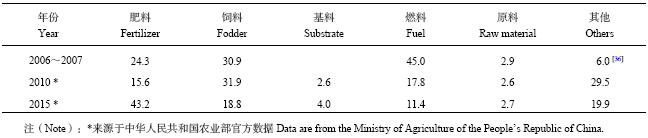
目前秸秆资源主要以工业原料、畜牧饲料、造肥还田和农村生活能源等方式被利用 (表11)。近年来,由于国家对农作物秸秆利用的补贴以及政策的引导,秸秆综合利用成效显著,2015年全国可收集秸秆资源量为9.0亿t,利用量为7.2亿t,秸秆综合利用率为80.1%。从利用途径看,秸秆作为肥料利用量为3.9亿t,占可收集资源量的43.2%;作为饲料利用量1.7亿t,占可收集资源量的18.8%;作为基料利用量为0.4亿t,占可收集资源量的4.0%;燃料量为1.0亿t,占可收集资源量的11.4%;作为原料利用量为0.2亿t,占可收集资源量的2.7%。虽然中国农作物秸秆综合利用率在提高,但秸秆养分资源可利用空间依然很大。秸秆还田作为秸秆资源利用方式,加大开发新型秸秆分解技术,将秸秆养分资源充分利用是实现化肥施用零增长行动和维持粮食稳产增产的潜在重要措施之一。
| 表11 中国秸秆资源利用变化 (%) Table 11 Changes in utilization of straw resources in China |
 |
随着中国化肥用量的增加,厩肥、绿肥和生活有机肥量的大幅度降低,秸秆已成为培肥土壤的重要有机肥源[177–178]。秸秆种类不同,其养分含量也有差别,有研究表明油料作物和豆科作物秸秆粗蛋白及粗脂肪含量高于粮食作物[179],过腹还田不适用于饲用价值不高的粮食作物秸秆[180]。中国秸秆还田的研究主要是北方小麦和玉米,南方主要是在水稻和小麦上。中国秸秆资源总量前三分别为长江中下游、华北和东北地区,这也是我国三大粮食作物的主产区,其资源量占到了27.9%、23.0%和19.0%,这些地区多为双季稻、稻麦轮作和冬小麦/夏玉米轮作区,作物种植茬口紧,秸秆还田量大,对机械要求较高,加速秸秆的腐解和养分释放是迫切需要解决的问题。
农田土壤中秸秆腐解伴随氮磷钾养分的释放是重要的生物地球化学过程,也是秸秆还田替代化肥养分的基础[181]。秸秆还田后总的腐解特征为前期快,后期较慢[182],秸秆的C/N比值在一定程度上影响秸秆腐解的速度,一般认为秸秆还田后C/N比调至25~30∶1即可满足分解过程中微生物对氮素的需要[183]。秸秆的含碳量较高,其中三大粮食作物秸秆的C/N比为50~70∶1,豆科植物和油料作物C/N比较低,一般为10~20∶1 [182, 184–186]。李昌明等[181]利用寒温带–暖温带–中亚热带的黑土、潮土、红壤互置试验平台,研究了小麦、玉米秸秆在3年腐解过程中的养分释放过程和影响因素,得出秸秆中养分释放速率的大小顺序为K > P > N;秸秆中氮素和磷素在寒温带以及在红壤和潮土中表现为先富集再释放特征,在暖温带、中亚热带以及黑土中表现为直接释放特征;秸秆中钾素均表现为直接快速释放特征,腐解0.5年平均释放率达89.5%。前期气候和土壤条件主导了氮磷的释放,在腐解后期 (2~3年) 土壤生物因素可能起了主导作用。马琳等[187]研究认为玉米秸秆腐解速度比小麦秸秆快,添加氮素可加快秸秆腐解和养分的释放。戴志刚等[188]利用盆栽试验研究了水稻土水稻秸秆、小麦秸秆、油菜秸秆在淹水培养下养分释放特征,结果表明,经过124天的培养,水稻秸秆、小麦秸秆、油菜秸秆的累积腐解率分别为49.2%、52.2%和49.8%。秸秆中养分释放速率均表现为K > P > C > N,释放量表现为C > K > N > P,水稻秸秆、小麦秸秆、油菜秸秆的碳释放率分别为7.5%、66.6%、52.5%,氮分别为42.0%、49.3%、57.8%,磷分别为68.3%、59.9%、67.3%,钾在培养12天后释放率均达到98.0%。可见,秸秆种类、土壤、气候和植被等因素均直接或间接影响秸秆的腐解和养分的释放。
秸秆还田可为作物生长提供养分,并提高土壤有机质含量和改善土壤理化形状,其与化肥配施可提高农田养分循环利用效率及肥料利用率[189]。秸秆还田存在腐解速率慢、养分释放延迟的问题[190]。丁文成等[191]利用盆栽试验研究了小麦–玉米–玉米轮作下潮土中15N标记的玉米秸秆中氮的有效性,结果表明15N标记玉米秸秆对当季冬小麦吸收氮的贡献平均为6.2%~14.2%,其当季回收率为7.1%~10.3%;第一茬和第二茬玉米对残留秸秆氮的回收率为3.8%~5.5%和 2.3%~3.2%,种植3季后约56%~69%的15N标记玉米秸秆氮残留在土壤中,损失 17%~26%,施氮肥越多秸秆氮的损失越多。单鹤翔等[192]的盆栽试验结果指出,氮肥用量为150和300 kg/hm2时冬小麦籽粒氮素来源于成熟玉米秸秆的比例为7%~10%,玉米秸秆氮素的当季回收率达到22.8%~33.1%。Laberge等[193]的田间微区试验表明,16.5年后生长2个月的大麦仍可回收到1.7%的残留豌豆秸秆氮。秸秆养分损失率低,大部分以有机态残留在土壤中,养分在土壤中累积[194],而化学养分易被植物吸收,损失率大[195]。因此,在秸秆长期还田下不仅需要考虑当季作物对秸秆养分的吸收,还需考虑秸秆养分的后效问题,而目前有关不同作物秸秆在不同土壤中养分有效性及其后效的相关研究较少。
秸秆还田是现代农业实践中的一项重要举措,研究表明,2/3左右秸秆还田可以有效改善土壤质量、缓解土壤养分流失、提高土壤供肥水平和土壤微生物活性[196],相对无秸秆还田可以增产5%~30%[197–202],同时可以减少10%~20%氮、磷、钾化肥用量,同时处理有机废弃物 6 250~22 500 kg/hm2[8]。秸秆还田后应该调整钾肥的施用时期与施用量,减少苗期基肥的施用量,增加追肥的用量,使作物整个生长期内钾素较为充裕;但是由于秸秆中氮、磷含量较低,释放速度相对较慢,秸秆还田腐解初期易产生微生物与作物竞争营养元素的现象,因此秸秆还田配施一定量的氮、磷肥是有必要的[188]。因此,在秸秆还田中需综合考虑秸秆种类、土壤、气候和植被等因素,了解秸秆养分释放规律及其有效性,以完善秸秆还田技术。
4 结论目前中国作物秸秆数量及其养分资源量依然巨大,2015年中国主要农作物秸秆资源量为71878.53万t,其中氮 (N)、磷 (P2O5)、钾 (K2O) 养分资源总量分别达到625.6万t、197.9万t、1159.5万t,秸秆养分还田是实现化肥减施增效的有效措施,具有广阔的应用前景。三大粮食作物秸秆产量仍然是秸秆资源主要组成部分,但其碳氮比比其他作物大,不利于微生物分解,而且做饲料适口性差。因此,改善秸秆还田方式及还田量,提高秸秆养分资源利用率是急需解决的问题,以提高秸秆资源充分利用,实现化肥施用零增长和保障国家粮食安全。
| [1] |
李逢雨, 孙锡发, 冯文强, 等. 麦秆、油菜秆还田腐解速率及养分释放规律研究[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(2): 374–380.
Li F Y, Sun X F, Feng W Q, et al. Nutrient release patterns and decomposing rates of wheat and rapeseed straw[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(2): 374–380. |
| [2] |
田慎重, 郭洪海, 董晓霞, 等. 耕作方式转变和秸秆还田对土壤活性有机碳的影响[J].
农业工程学报, 2016, 32(2): 39–45.
Tian S Z, Guo H H, Dong X X, et al. Effect of tillage method change and straw return on soil labile organic carbon[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(2): 39–45. |
| [3] |
郝翔翔, 杨春葆, 苑亚茹, 等. 连续秸秆还田对黑土团聚体中有机碳含量及土壤肥力的影响[J].
中国农学通报, 2013, 29(35): 263–269.
Hao X X, Yang C B, Yuan Y R, et al. Effects of continuous straw returning on organic carbon content in aggregates and fertility of black soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(35): 263–269. DOI:10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2013-0286 |
| [4] |
武均, 蔡立群, 罗迪, 等. 不同耕作措施对陇中黄土高原雨养农田土壤团聚体稳定性和 C、N、P的影响[J].
水土保持学报, 2014, 28(6): 234–239.
Wu J, Cai L Q, Luo D, et al. Effects of different tillage methods on the content of SOC, TN, TP in soil aggregates of rain-fed field of the loess plateau in central of Gansu[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(6): 234–239. |
| [5] |
谭德水, 金继运, 黄绍文, 等. 灌淤土区长期施钾对作物产量与养分及土壤钾素的长期效应研究[J].
中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(4): 625–629.
Tan D S, Jin J Y, Huang S W, et al. Effect of long-term potassium application on irrigated soil potassium and on the yield and nutrient of crops[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2009, 17(4): 625–629. |
| [6] |
吴婕, 朱钟麟, 郑家国, 等. 秸秆覆盖还田对土壤理化性质及作物产量的影响[J].
西南农业学报, 2006, 19(2): 192–195.
Wu J, Zhu Z L, Zheng J G, et al. Influences of straw mulching treatment on soil physical and chemical properties and crop yields[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 19(2): 192–195. |
| [7] |
刘禹池, 冯文强, 秦鱼生, 等. 长期秸秆还田与施肥对成都平原稻麦轮作下作物产量和土壤肥力的影响[J].
西南农业学报, 2015, 28(1): 240–247.
Liu Y C, Feng W Q, Qin Y S, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization and straw mulch on crop yields and soil fertility under rice-wheat rotation in Chengdu Plain[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 28(1): 240–247. |
| [8] |
李明德, 吴海勇, 聂军, 等. 稻草及其循环利用后的有机废弃物还田效用研究[J].
中国农业科学, 2010, 43(17): 3572–3579.
Li M D, Wu H Y, Nie J, et al. Utilities of straw and wastes of straw recycling returning on rice planting[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(17): 3572–3579. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.17.011 |
| [9] |
王振忠, 吴敬民, 陈留根, 等. 稻麦两熟地区秸秆全量直接还田施肥技术的增产培肥效果[J].
江苏农业学报, 2003, 19(3): 151–156.
Wang Z Z, Wu J M, Chen L G, et al. Effects of direct and whole straw manuring method on increasing yield of crop and fertility of soil in rice-wheat double cropping area of Taihu Lake district[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2003, 19(3): 151–156. |
| [10] |
徐泰平, 朱波, 汪涛, 等. 秸秆还田对紫色土坡耕地养分流失的影响[J].
水土保持学报, 2006, 20(1): 30–32.
Xu T P, Zhu B, Wang T, et al. Effects of returned straw on nutrient loss from slope cropland of purple soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 20(1): 30–32. |
| [11] |
陈浩, 李小刚, 周游, 等. 农作物秸秆还田资源化利用研究进展[J].
湖南农业科学, 2015, (6): 138–141.
Chen H, Li X G, Zhou Y, et al. Research advance in the resource utilization of returning straw[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2015, (6): 138–141. |
| [12] |
孟军, 张伟明, 王绍斌, 等. 农林废弃物炭化还田技术的发展与前景[J].
沈阳农业大学学报, 2011, 42(4): 387–392.
Meng J, Zhang W M, Wang S B, et al. Development and prospect of carbonization and returning technology of agro-forestry residue[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2011, 42(4): 387–392. |
| [13] |
花莉, 张成, 马宏瑞, 等. 秸秆生物质炭土地利用的环境效益研究[J].
生态环境学报, 2010, 19(10): 2489–2492.
Hua L, Zhang C, Ma H R, et al. Environmental benefits of biochar made by agricultural straw when applied to soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(10): 2489–2492. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.10.040 |
| [14] | Pathak H, Singh R, Bhatia A, et al. Recycling of rice straw to improve wheat yield and soil fertility and reduce atmospheric pollution[J]. Paddy & Water Environment, 2006, 4(2): 111–117. |
| [15] | Whitbread A, Blair G, Konboon Y, et al. Managing crop residues, fertilizers and leaf litters to improve soil C, nutrient balances, and the grain yield of rice and wheat cropping systems in Thailand and Australia[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2003, 100(2-3): 251–263. |
| [16] |
方放, 王飞, 石祖梁, 等. 京津冀秸秆养分资源及秸秆焚烧气体污染物排放定量估算[J].
农业工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 1–6.
Fang F, Wang F, Shi Z L, et al. Quantitative estimation on straw nutrient resources and emission of pollutants from straw burning in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(3): 1–6. |
| [17] |
包建财, 郁继华, 冯致, 等. 西部七省区作物秸秆资源分布及利用现状[J].
应用生态学报, 2014, 25(1): 181–187.
Bao J C, Yu J H, Feng Z, et al. Situation of distribution and utilization of crop straw resources in seven western provinces, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(1): 181–187. |
| [18] |
戴志刚, 鲁剑巍, 周先竹, 等. 中国农作物秸秆养分资源现状及利用方式[J].
湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(1): 27–29.
Dai Z G, Lu J W, Zhou X Z, et al. The present situation and utilization mode of crop residue nutritious resources[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 52(1): 27–29. |
| [19] |
朱开伟, 刘贞, 欧训民, 等. 基于土壤功能的中国主要农作物可能源化秸秆生态潜力分析[J].
中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(2): 276–286.
Zhu K W, Liu Z, Ou X M, et al. Evaluation of energy-oriented utilization potential of main Chinese crop residues based on soil protection functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(2): 276–286. |
| [20] |
左旭, 王红彦, 王亚静, 等. 中国玉米秸秆资源量估算及其自然适宜性评价[J].
中国农业资源与区划, 2015, 36(6): 5–10.
Zuo X, Wang H Y, Wang Y J, et al. Estimation and suitability evaluation of corn straw resources in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2015, 36(6): 5–10. DOI:10.7621/cjarrp.1005-9121.20150602 |
| [21] |
彭春艳, 罗怀良, 孔静. 中国作物秸秆资源量估算与利用状况研究进展[J].
中国农业资源与区划, 2014, (3): 14–20.
Peng C Y, Luo H L, Kong J. Advance in estimation and utilization of crop residues resources in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning,, 2014, (3): 14–20. DOI:10.7621/cjarrp.1005-9121.20140303 |
| [22] |
杨轶囡, 吴迪, 刘文明, 等. 吉林省玉米秸秆资源化利用的问题与对策研究[J].
玉米科学, 2016, (2): 171–174.
Yang Y N, Wu D, Liu W M, et al. Maize straw resource utilization and countermeasures in Jilin province[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2016, (2): 171–174. |
| [23] |
方放, 李想, 石祖梁, 等. 黄淮海地区农作物秸秆资源分布及利用结构分析[J].
农业工程学报, 2015, 31(2): 228–234.
Fang F, Li X, Shi Z L, et al. Analysis on distribution and use structure of crop straw resources in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(2): 228–234. |
| [24] |
姚宗路, 赵立欣, 田宜水, 等. 黑龙江省农作物秸秆资源利用现状及中长期展望[J].
农业工程学报, 2009, 25(11): 288–292.
Yao Z L, Zhao L X, Tian Y S, et al. Utilization status and medium and long-term forecast of crop straw in Heilongjiang province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(11): 288–292. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.11.053 |
| [25] |
王如芳, 张吉旺, 董树亭, 等. 我国玉米主产区秸秆资源利用现状及其效果[J].
应用生态学报, 2011, 22(6): 1504–1510.
Wang R F, Zhang J W, Dong S T, et al. Present situation of maize straw resource utilization and its effect in main maize production regions of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(6): 1504–1510. |
| [26] |
李彬, 高翔, 刘玉涛, 等. 江苏水稻秸秆资源饲料化利用技术研究[J].
中国农机化学报, 2017, 38(5): 100–105.
Li B, Gao X, Liu Y T, et al. Study on feed utilization technology of rice straw in Jiangsu province[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2017, 38(5): 100–105. |
| [27] |
顾克军, 杨四军, 张斯梅, 等. 不同生产条件下留茬高度对水稻秸秆可收集量的影响[J].
中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(4): 831–835.
Gu K J, Yang S J, Zhang S M, et al. Effect of stubble height on collectable amount of rice straw under different cultivation patterns[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2011, 19(4): 831–835. |
| [28] |
李书田, 金继运. 中国不同区域农田养分输入、输出与平衡[J].
中国农业科学, 2011, 44(20): 4207–4229.
Li S T, Jin J Y. Characteristics of nutrient input/output and nutrient balance in different regions of China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(20): 4207–4229. |
| [29] |
杨晓光, 刘志娟, 陈阜. 全球气候变暖对中国种植制度可能影响: VI. 未来气候变化对中国种植制度北界的可能影响[J].
中国农业科学, 2011, 44(8): 1562–1570.
Yang X G, Liu Z J, Chen F. The possible effects of global warming on cropping systems in China. VI. Possible effects of future climate change on northern limits of cropping system in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(8): 1562–1570. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.08.004 |
| [30] |
卢布, 丁斌, 吕修涛, 等. 中国小麦优势区域布局规划研究[J].
中国农业资源与区划, 2010, 31(2): 6–12.
Lu B, Ding B, Lu X T, et al. Arrangement planning of Chinese wheat ascendant regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2010, 31(2): 6–12. |
| [31] |
孙华生, 黄敬峰, 李波, 等. 中国水稻遥感信息获取区划研究[J].
中国农业科学, 2008, 41(12): 4039–4047.
Sun H S, Huang J F, Li B, et al. Study on the regionalization of paddy rice information acquirement through remote sensing technology in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(12): 4039–4047. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.12.013 |
| [32] |
全国农业技术推广服务中心. 中国有机肥料资源[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1999.
China National Agricultural Technology Extension Service. Data collection for organic fertilizer nutrients in China [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1999. |
| [33] |
张培栋, 杨艳丽, 李光全, 等. 中国农作物秸秆能源化潜力估算[J].
可再生能源, 2007, 25(6): 80–83.
Zhang P D, Yang Y L, Li G Q, et al. Energy potentiality of crop straw resources in China[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2007, 25(6): 80–83. |
| [34] |
刘刚, 沈镭. 中国生物质能源的定量评价及其地理分布[J].
自然资源学报, 2007, 22(1): 132.
Liu G, Shen L. Quantitive appraisal of biomass energy and its geographical distribution in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2007, 22(1): 132. |
| [35] |
谢光辉, 韩东倩, 王晓玉, 等. 中国禾谷类大田作物收获指数和秸秆系数[J].
中国农业大学学报, 2011, 16(1): 1–8.
Xie G H, Han D Q, Wang X Y, et al. Harvest index and residue factor of cereal crops in China[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2011, 16(1): 1–8. |
| [36] |
高利伟, 马林, 张卫峰, 等. 中国作物秸秆养分资源数量估算及其利用状况[J].
农业工程学报, 2009, 25(7): 173–179.
Gao L W, Ma L, Zhang W F, et al. Estimation of nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its utilization situation in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(7): 173–179. |
| [37] |
钟华平, 岳燕珍, 樊江文. 中国作物秸秆资源及其利用[J].
资源科学, 2003, 25(4): 62–67.
Zhong H P, Yue Y Z, Fan J W. Characteristics of crop straw resources in China and its utilization[J]. Resources Science, 2003, 25(4): 62–67. |
| [38] |
王琛, 胡玉福, 魏晋, 等. 区域农业废弃物资源存量估算及利用现状[J].
四川农业大学学报, 2011, 29(1): 119–123.
Wang C, Hu Y F, Wei J, et al. Study on stock estimation and utilization status of agricultural residue resources at a county[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2011, 29(1): 119–123. |
| [39] |
毕于运, 高春雨, 王亚静, 等. 中国秸秆资源数量估算[J].
农业工程学报, 2009, 25(12): 211–217.
Bi Y Y, Gao C Y, Wang Y J, et al. Estimation of straw resources in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(12): 211–217. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.12.037 |
| [40] |
中华人民共和国国家统计局农村社会经济调查总队. 新中国五十年农业统计资料[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2000.
National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Fifty years of agricultural statistics in New China[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2000. |
| [41] |
韩鲁佳, 闫巧娟, 刘向阳, 等. 中国农作物秸秆资源及其利用现状[J].
农业工程学报, 2002, 18(3): 87–91.
Han L J, Yan Q J, Liu X Y, et al. Straw resources and their utilization in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2002, 18(3): 87–91. |
| [42] |
毕于运. 秸秆资源评价与利用研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院博士学位论文, 2010.
Bi Y Y. Study on straw resources evaluation and utilization in China [D]. Beijing: PhD Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2010. |
| [43] |
张福春, 朱志辉. 中国作物的收获指数[J].
中国农业科学, 1990, 23(2): 83–87.
Zhang F C, Zhu Z H. Harvest index for various crops in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1990, 23(2): 83–87. |
| [44] | Buresh R J, Pampolino M F, Witt C. Field-specific potassium and phosphorus balances and fertilizer requirements for irrigated rice-based cropping systems[J]. Plant and Soil, 2010, 335(1-2): 35–64. DOI:10.1007/s11104-010-0441-z |
| [45] | Liu M, Yu Z, Liu Y, et al. Fertilizer requirements for wheat and maize in China: the QUEFTS approach[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2006, 74(3): 245–258. DOI:10.1007/s10705-006-9002-5 |
| [46] |
张兴梅, 蔡德利, 王法清, 等. 不同大豆品种在养分吸收及产量上的比较[J].
中国土壤与肥料, 2004, (3): 41–42.
Zhang X M, Cai D L, Wang F Q, et al. Comparison of nutrient uptake and yield of different varieties of soybean[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2004, (3): 41–42. DOI:10.11838/sfsc.20040313 |
| [47] | Salvagiotti F, Cassman K G, Specht J E, et al. Nitrogen uptake, fixation and response to fertilizer N in soybeans: A review[J]. Field Crops Research, 2008, 108(1): 1–13. DOI:10.1016/j.fcr.2008.03.001 |
| [48] |
段玉, 张君, 李焕春, 等. 马铃薯氮磷钾养分吸收规律及施肥肥效的研究[J].
土壤, 2014, 46(2): 212–217.
Duan Y, Zhang J, Li H C, et al. Fertilization effect and nutrition use efficiency of potato in Inner Mongolia[J]. Soils, 2014, 46(2): 212–217. |
| [49] |
周可金, 马成泽, 许承保, 等. 施钾对花生养分吸收、产量与效益的影响[J].
应用生态学报, 2003, 14(11): 1917–1920.
Zhou K J, Ma C Z, Xu C B, et al. Effects of potash fertilizer on nutrient absorption by peanut and its yield and benefit[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(11): 1917–1920. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.11.024 |
| [50] |
邹娟, 鲁剑巍, 刘锐林, 等. 4个双低甘蓝型油菜品种干物质积累及养分吸收动态[J].
华中农业大学学报, 2008, 27(2): 229–234.
Zou J, Lu J W, Liu R L, et al. Dynamics of dry mass accumulation and nutrients uptake in 4 double-low rapeseed (Brassica napus L) varieties [J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2008, 27(2): 229–234. |
| [51] |
侯云鹏, 韩立国, 孔丽丽, 等. 不同施氮水平下水稻的养分吸收、转运及土壤氮素平衡[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(4): 836–845.
Hou Y P, Han L G, Kong L L, et al. Nutrient absorption, translocation in rice and soil nitrogen equilibrium under different nitrogen application doses[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(4): 836–845. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2015.0402 |
| [52] |
杨继学, 黄珊珊, 杨明亮, 等. 密度和施肥量对不同分枝类型大豆产量的影响[J].
大豆科学, 2012, 31(3): 381–384.
Yang J X, Huang S S, Yang M L, et al. Effect of density and fertilizer amount on yield of different branching types of soybeans[J]. Soybean Science, 2012, 31(3): 381–384. |
| [53] |
周敬霄. 密度及氮磷钾施肥量对夏大豆邯豆5号产量影响[J].
大豆科技, 2011, (2): 13–16.
Zhou J X. The influence of planting density and different NPK on the yield of Handou No. 5[J]. Soybean Bulletin, 2011, (2): 13–16. |
| [54] |
王志刚, 高强, 冯国忠. 吉林省大豆施肥指标体系初步建立[J].
大豆科学, 2010, 29(4): 669–672.
Wang Z G, Gao Q, Feng G Z. Preliminary raising fertilization index system for soybean in Jilin province[J]. Soybean Science, 2010, 29(4): 669–672. |
| [55] |
杨继学. 不同类型大豆品种在不同密度和肥力下的高产潜力研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学硕士学位论文, 2012.
Yang J X. The sdudy of high yield potency in different types of cultivas under different density and fertility on soybean [D]. Harbin: MS Thesis of Northeast Agriculture University, 2012. |
| [56] |
范荣, 杜霄, 白宏鹏. 旱地大豆全膜覆土穴播最佳施肥量试验总结[J].
农业科技与信息, 2012, (15): 6–7.
Fan R, Du X, Bai H P. A summary of the experiment on the best fertilizer application of soybean mulched with plastic film in dry land[J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, 2012, (15): 6–7. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6997.2012.15.002 |
| [57] |
张瑞, 崔萌萌, 冯洁琼. 不同播种期、施肥量和种植密度对秋大豆十月黄产量的影响[J].
上海蔬菜, 2016, (2): 34–35.
Zhang R, Cui M M, Feng J Q. Effects of different sowing time, fertilizer amount and planting density on yield of autumn soybean[J]. Shanghai Vegetables, 2016, (2): 34–35. |
| [58] |
李文龙, 李喜焕, 王瑞霞, 等. 河北省夏播极早熟区施肥与密度对大豆农艺性状和品质的影响[J].
河北农业科学, 2015, (1): 10–13.
Li W L, Li X H, Wang R X, et al. Effects of fertilizer and planting density on agronomic traits and quality of soybean in extremely early mature soybean region of Hebei province[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2015, (1): 10–13. |
| [59] |
李文龙, 李喜焕, 王瑞霞, 等. 河北省夏播早熟区不同施肥水平和种植密度对大豆产量及品质的影响[J].
河南农业科学, 2015, 44(3): 40–44.
Li W L, Li X H, Wang R X, et al. Effects of different fertilizer levels and planting densities on yield and quality of soybean in early mature soybean region of Hebei[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 44(3): 40–44. |
| [60] |
王斌斌, 朱洪德, 唐培坤, 等. 不同肥密对高油大豆品种产量的影响[J].
现代化农业, 2015, (10): 16–17.
Wang B B, Zhu H D, Tang P K, et al. Effects of different fertilizers on yield of high oil soybean varieties[J]. Modernizing Agriculture, 2015, (10): 16–17. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2015.10.007 |
| [61] |
姬景红, 李玉影, 刘双全, 等. 平衡施肥对松嫩平原黑土区大豆产量效益的影响[J].
大豆科学, 2010, 29(5): 820–825.
Ji J H, Li Y Y, Liu S Q, et al. Effect of balanced fertilization on yield of soybean and nutrients balance of soil-crop system[J]. Soybean Science, 2010, 29(5): 820–825. |
| [62] |
张明怡, 刘颖, 李玉影, 等. 施肥对大豆产量、效益及养分平衡影响的研究[J].
中国土壤与肥料, 2010, (3): 31–33.
Zhang M Y, Liu Y, Li Y Y, et al. The effect of balanced fertilization on yield of soybean and nutrient input-output in soil crop system[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2010, (3): 31–33. |
| [63] |
苗任重, 任秀荣, 王建立, 等. 氮磷钾肥配施对大豆生长发育及产量的影响[J].
湖南农业科学, 2014, (5): 29–31.
Miao R Z, Ren X R, Wang J L, et al. Effects of combined application of NPK fertilizers on growth and yield of soybean[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2014, (5): 29–31. |
| [64] |
魏丹, 李艳, 李玉梅, 等. 氮磷钾元素对黑龙江不同地区大豆产量和品质的影响[J].
大豆科学, 2017, 36(1): 87–91.
Wei D, Li Y, Li Y M, et al. Effect of N, P, K fertilization on yield and quality of soybean in Heilongjiang province[J]. Soybean Science, 2017, 36(1): 87–91. |
| [65] |
李玉影, 刘双全, 姬景红, 等. 黑龙江省不同农业生态区大豆平衡施肥效果研究[J].
大豆科学, 2015, 34(6): 1029–1038.
Li Y Y, Liu S Q, Ji J H, et al. Study on the effect of balanced fertilization of soybean in different agricultural ecological regions of Heilongjang province[J]. Soybean Science, 2015, 34(6): 1029–1038. |
| [66] |
刘润梅, 范茂攀, 付云章, 等. 云南省马铃薯施肥量与化肥偏生产力的关系研究[J].
土壤学报, 2014, (4): 753–760.
Liu R M, Fan M P, Fu Y Z, et al. Relationship between fertilization rate and fertilizer partial factor productivity in potato production in Yunnan province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014, (4): 753–760. |
| [67] |
杨德桦. 不同施肥量和不同施肥方式对襄阳地区马铃薯产量、养分积累规律和品质的影响[D]. 湖北武汉: 华中农业大学硕士学位论文, 2012.
Yang D H. Effect of different fertilizer rates and fertilization methods on yield, nutrients accumulation and tuber quality of potato in Xiangyang [D]. Wuhan, Hubei: MS Thesis of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012 |
| [68] |
戴树荣. 应用" 3414”试验设计建立二次肥料效应函数寻求马铃薯氮磷钾适宜施肥量的研究[J].
中国农学通报, 2010, 26(12): 154–159.
Dai S R. NPK Reasonable application rate on potato by establishing fertilizer effect model of second degree polynomial using " 3414” experimental design[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(12): 154–159. |
| [69] |
谭乾开, 黎华寿, 林洁, 等. 不同施肥配方对冬种马铃薯农艺性状和产量质量的影响研究[J].
中国农学通报, 2012, 28(33): 166–171.
Tan Q K, Li H S, Lin J, et al. Effect of different fertilization level on the agronomic traits and yield of potato[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(33): 166–171. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.33.033 |
| [70] |
张平良, 郭天文, 李书田, 等. 不同覆盖种植方式与平衡施肥对马铃薯产量及水分利用效率的影响[J].
干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(1): 50–54.
Zhang P L, Guo T W, Li S T, et al. Effects of different coverage cultivation and balanced fertilization on yield and water use efficiency of potato in the dry-land[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(1): 50–54. DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2017.01.08 |
| [71] |
何文寿, 马琨, 代晓华, 等. 宁夏马铃薯氮、磷、钾养分的吸收累积特征[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(6): 1477–1487.
He W S, Ma K, Dai X H, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake and accumulation of potato in Ningxia[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(6): 1477–1487. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2014.0618 |
| [72] |
杨胜先, 龙国, 张绍荣, 等. 喀斯特冷凉山区不同种植密度及氮、磷、钾配施对马铃薯产量的影响[J].
江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(7): 85–88.
Yang S X, Long G, Zhang S R, et al. Effects of different planting density and nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on yield of potato in Karst[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(7): 85–88. |
| [73] |
王涛, 何文寿, 姜海刚, 等. 氮磷钾不同用量对马铃薯产量和淀粉含量的影响[J].
中国土壤与肥料, 2016, (3): 80–86.
Wang T, He W S, Jiang H G, et al. The effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium application on yield and starch content of potato plants[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016, (3): 80–86. DOI:10.11838/sfsc.20160313 |
| [74] |
马俊伟, 涂新红, 何远杰, 等. 粤北地区花生氮磷钾" 3414”肥料效应试验[J].
安徽农学通报, 2017, 23(6): 81–82.
Ma J W, Tu X H, He Y J, et al. The " 3414” fertilizer effect of peanut in northern Guangdong province[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 23(6): 81–82. |
| [75] |
王红军, 张静, 皇甫自起, 等. 豫东平原高产花生施用氮磷钾肥增产效应研究[J].
中国农学通报, 2017, 33(13): 1–5.
Wang H J, Zhang J, Huangfu Z Q, et al. Yield-increasing effect of NPK fertilizer on high-yield peanut in east Henan plain[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(13): 1–5. |
| [76] |
徐文霞, 刘听报. 新野县夏花生氮肥最佳经济施用量试验研究[J].
现代农业科技, 2016, (2): 19.
Xu W X, Liu T B. Experimental study on optimum economic application rate of summer peanut nitrogen in Xinye County[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, (2): 19. |
| [77] |
司贤宗, 张翔, 毛家伟, 等. 高产夏花生养分限制因子及养分吸收积累研究[J].
河南农业科学, 2016, 45(11): 34–37.
Si X Z, Zhang X, Mao J W, et al. Nutrient restricting factors and accumulation of high-yield summer peanut[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 45(11): 34–37. |
| [78] |
张桥, 张育灿, 林日强, 等. 广东省花生测土配方施肥氮素指标体系研究[J].
中国农学通报, 2014, 30(33): 101–104.
Zhang Q, Zhang Y C, Lin R Q, et al. Research of nitrogen in formula fertilization by soil testing index system for peanut in Guangdong[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(33): 101–104. |
| [79] |
金昆, 邱源. 自贡市贡井区花生" 3414”试验报告[J].
南方农业, 2015, 9(6): 17–18.
Jin K, Qiu Y. Test report on peanut " 3414” in Gongjing district of Zigong city[J]. South China Agriculture, 2015, 9(6): 17–18. |
| [80] |
龚永锋, 刘鲜珍, 李利民, 等. 宁远县丘陵红壤旱地花生" 3414”田间肥效试验[J].
现代农业科技, 2015, (7): 33–34.
Gong Y F, Liu X Z, Li L M, et al. Effect of field fertilizer on peanut using " 3414” in dryland of red soil in Ningyuan county[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, (7): 33–34. |
| [81] |
颜明娟, 章明清, 李娟, 等. 福建花生测土配方施肥指标体系研究[J].
中国油料作物学报, 2010, 32(3): 424–430.
Yan M J, Zhang M Q, Li J, et al. Soil testing and formula fertilization index for peanut in Fujian province[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2010, 32(3): 424–430. |
| [82] |
张桂兴, 严学东, 康轩, 等. 花生测土配方施肥试验研究[J].
现代农业科技, 2016, (16): 17.
Zhang G X, Yan X D, Kang X, et al. Experimental study on fertilization test of peanut soil test[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, (16): 17. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.16.006 |
| [83] |
郑荔敏. 花生测土配方施肥指标体系研究[J].
福建农业科技, 2016, (10): 7–10.
Zheng L M. Study on index system of soil testing and formulated fertilization for peanut[J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, (10): 7–10. |
| [84] |
祁大成, 冯旭东, 董红梅, 等. 花生" 3414”肥料效应试验及推荐施肥分析[J].
湖北农业科学, 2011, 50(14): 2831–2834.
Qi D C, Feng X D, Dong H M, et al. " 3414” fertilizer trial of peanut and analysis on the optimal fertilization amounts[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 50(14): 2831–2834. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2011.14.007 |
| [85] |
邹娟. 冬油菜施肥效果及土壤养分丰缺指标研究[D]. 湖北武汉: 华中农业大学博士学位论文, 2010.
Zhou J. Study on response of winter rapeseed to NPKB fertilization and abundance & deficiency indices of soil nutrients[D]. Wuhan, Hubei: PhD Dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010. |
| [86] |
黄亿, 李廷轩, 张锡洲, 等. 基于" 3414”试验的川中丘陵区油菜施肥指标体系构建[J].
中国农业科学, 2013, 46(10): 2058–2066.
Huang Y, Li T X, Zhang X Z, et al. Establishiment of fertilization recommendation indexes of rapeseed soil based on the " 3414” field experiments in the middle of Sichuan hilly regions[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(10): 2058–2066. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.10.011 |
| [87] |
朱克保, 吴传洲, 奚波, 等. 应用" 3414”试验建立芜湖县油菜施肥指标体系[J].
中国农学通报, 2010, 26(19): 155–160.
Zhu K B, Wu C Z, Xi B, et al. Establishing fertilization recommendation index of rapeseed in Wuhu County based on the " 3414” field experiments[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(19): 155–160. |
| [88] |
许福涛, 顾黄辉, 徐军. 海门市油菜氮磷钾肥料效应研究Ⅱ: 施肥效益[J].
土壤, 2012, 44(2): 237–241.
Xu F T, Gu H H, Xu J. Response of rape to N, P and K fertilizer in Haimen: fertilizing benefits[J]. Soils, 2012, 44(2): 237–241. |
| [89] |
邹小云, 陈伦林, 李书宇, 等. 氮、磷、钾、硼肥施用对甘蓝型杂交油菜产量及经济效益的影响[J].
中国农业科学, 2011, 44(5): 917–924.
Zou X Y, Chen L L, Li S Y, et al. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and boron fertilizers on yield and profit of hybrid rapeseed[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(5): 917–924. |
| [90] |
张萌, 王寅, 任涛, 等. 施肥对贵州直播油菜产量和养分吸收的影响[J].
中国油料作物学报, 2014, (3): 369–373.
Zhang M, Wang Y, Ren T, et al. Effects of fertilization on yield and nutrient uptake of direct-sowing oilseed rape in Guizhou province[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2014, (3): 369–373. DOI:10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2014.03.012 |
| [91] |
杨俐苹, 白由路, 王贺, 等. 测土配方施肥指标体系建立中" 3414”试验方案应用探讨[A]. 中国植物营养与肥料学会2010年学术年会论文集[C]. 北京: 中国植物营养与肥料学会, 2010.
Yang L P, Bai Y L, Wang H, et al. Application of " 3414” field trial design for establishing soil testing and fertilizer recommendation index [A]. Chinese Society of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Sciences Proceeding of Annual Conference 2010[C]. Beijing: Chinese Society of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Sciences, 2010. |
| [92] |
刘炜, 谷思玉, 白雅梅, 等. 施肥量与灌溉量对黑龙江省黑土区水稻产量的影响[J].
东北农业大学学报, 2012, 43(4): 49–54.
Liu W, Gu S Y, Bai Y M, et al. Effect of fertilizer levels and irrigation on yield of rice in black soil area[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2012, 43(4): 49–54. |
| [93] |
姬景红, 李玉影, 刘双全, 等. 平衡施肥对玉米产量、效益及土壤作物系统养分收支的影响[J].
中国土壤与肥料, 2010, (4): 37–41.
Ji J H, Li Y Y, Liu S Q, et al. The effect of balanced fertilization on yield, benefit of corn and nutrient balance[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2010, (4): 37–41. |
| [94] |
串丽敏. 基于产量反应和农学效率的小麦推荐施肥方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院博士学位论文, 2013.
Chuan L M. Methodology of fertilizer recommendation based on yield response and agronomic efficiency for wheat [D]. Beijing: PhD Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. |
| [95] |
耿以工, 李洪山, 丁振云. 天津市冬小麦节水栽培条件下施氮量的效应研究[J].
河北农业科学, 2011, 15(7): 13–15.
Geng Y G, Li H S, Ding Z Y. Effects of nitrogen application level on water-saving cultivation of winter wheat in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 15(7): 13–15. |
| [96] |
马志强, 黄智谋, 刘伟, 等. 不同施钾量对中单509玉米植株性状及产量的影响[J].
现代农业科技, 2017, (1): 1–3.
Ma Z Q, Huang Z M, Liu W, et al. Effect of different potash levels on yield and plant traits of maize Zhongdan 509[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, (1): 1–3. |
| [97] |
王永华, 黄源, 辛明华, 等. 周年氮磷钾配施模式对砂姜黑土麦玉轮作体系籽粒产量和养分利用效率的影响[J].
中国农业科学, 2017, 50(6): 1031–1046.
Wang Y H, Huang Y, Xin M H, et al. Effects of the year-round management model of N, P and K combined application on grain yield and nutrient efficiency of wheat-maize rotation system in lime concretion black soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(6): 1031–1046. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.06.005 |
| [98] |
黄立梅, 黄绍文, 韩宝文. 冬小麦–夏玉米适宜氮磷用量和平衡施肥效应[J].
中国土壤与肥料, 2010, (5): 38–44.
Huang L M, Huang S W, Han B W. Winter wheat–summer corn response to nitrogen and phosphorus application and balanced fertilization[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2010, (5): 38–44. |
| [99] |
沙之敏, 边秀举, 郑伟, 等. 最佳养分管理对华北冬小麦养分吸收和利用的影响[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(5): 1049–1055.
Sha Z M, Bian X J, Zheng W, et al. Effects of optimum nutrient management on nutrient uptake and utilization of winter wheat in North China plain[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(5): 1049–1055. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2010.0502 |
| [100] |
王宜伦, 李潮海, 何萍, 等. 超高产夏玉米养分限制因子及养分吸收积累规律研究[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 559–566.
Wang Y L, Li C H, He P, et al. Nutrient restrictive factors and accumulation of super-high-yield summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(3): 559–566. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2010.0307 |
| [101] |
王红军, 张静, 皇甫自起, 等. 豫东平原超高产夏玉米测土配方施肥技术参数研究[J].
土壤与作物, 2017, 6(1): 55–60.
Wang H J, Zhang J, Huangfu Z Q, et al. Parameter determination to formula fertilization by soil testing for super high-yield maize: A case study in Yudong plain, Henan Province[J]. Soils and Crops, 2017, 6(1): 55–60. DOI:10.11689/j.issn.2095-2961.2017.01.009 |
| [102] |
文德泽. 不同施肥处理对晋南旱地小麦产量及水肥利用的影响[D]. 山西太谷: 山西农业大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
Wen D Z. Effects of different fertilization on dry plateau wheat yield and water fertilizer use in southern Shanxi [D]. Taigu, Shanxi: MS Thesis of Shanxi Agricultural University, 2015. |
| [103] |
郭玲玲. " 3414”测土配方施肥对玉米产量和养分吸收的影响[J].
山西农业科学, 2015, 43(5): 576–578.
Guo L L. Effect of " 3414” formula fertilization on yield and nutrient absorption of maize[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(5): 576–578. |
| [104] |
杨峰, 闫秋艳, 鲁晋秀, 等. 氮肥运筹对夏玉米产量、氮素利用率及土壤养分残留量的影响[J].
华北农学报, 2017, 32(1): 171–178.
Yang F, Yan Q Y, Lu J X, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on summer maize yield, nutrient utilization efficiency and soil available nutrient residues[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2017, 32(1): 171–178. DOI:10.7668/hbnxb.2017.01.026 |
| [105] |
程秋华, 陆萍, 冯建忠, 等. 水稻氮、磷、钾" 3414”肥效试验初报[J].
上海农业学报, 2012, 28(2): 137–142.
Cheng Q H, Lu P, Feng J Z, et al. Preliminary study on effects of N, P and K on rice by " 3414” fertilizer test[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2012, 28(2): 137–142. |
| [106] |
陈小倩, 石建福, 诸海焘, 等. " 3414”肥料效应试验在东滩小麦上的应用初探[J].
上海农业科技, 2014, (5): 118–119.
Chen X Q, Shi J F, Zhu H T, et al. Application of " 3414” fertilizer effect experiment on Dongtan wheat[J]. Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014, (5): 118–119. |
| [107] |
李鸿伟, 杨凯鹏, 曹转勤, 等. 稻麦连作中超高产栽培小麦和水稻的养分吸收与积累特征[J].
作物学报, 2013, 39(3): 464–477.
Li H W, Yang K P, Cao Z Q, et al. Characteristics of nutrient uptake and accumulation in wheat and rice with continuous cropping under super-high-yielding cultivation[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 464–477. |
| [108] |
于林惠, 李刚华, 徐晶晶, 等. 机插粳稻氮磷钾吸收分配特征[J].
作物学报, 2012, 38(4): 707–716.
Yu L H, Li G H, Xu J J, et al. Characteristics of uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and partitioning in mechanical transplanting japonica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(4): 707–716. |
| [109] |
殷建华, 孙同林. 小麦平衡施肥参数试验初探[J].
上海农业科技, 2010, (3): 72–73.
Yin J H, Sun T L. Study on balanced fertilizer application in wheat parameter test[J]. Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2010, (3): 72–73. |
| [110] |
董作珍, 吴良欢, 柴婕, 等. 不同氮磷钾处理对中浙优1号水稻产量、品质、养分吸收利用及经济效益的影响[J].
中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 399–407.
Dong Z Z, Wu L H, Cai J, et al. Effects of different nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium treatments on rice yield, quality, nutrient absorption-utilization and economic benefit of Zhongzheyou 1 in central Zhejiang province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 399–407. |
| [111] |
张国荣, 谷思玉, 李菊梅, 等. 长江中下游地区高产稻田施肥与产量的关系[J].
中国土壤与肥料, 2010, (1): 75–80.
Zhang G R, Gu S Y, Li J M, et al. The relationship between fertilization and yield of high-yield paddy field in middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2010, (1): 75–80. |
| [112] |
雷之萌, 韩上, 武际, 等. 淮北砂姜黑土区氮钾配施对小麦产量及氮、钾养分吸收利用的影响[J].
农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(2): 161–167.
Lei Z M, Han S, Wu J, et al. Effects of combined application of nitrogen and potassiumon on yield and nutrient accumulation of wheat in Huaibei lime concretion black soil area, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017, 34(2): 161–167. |
| [113] |
王伟妮. 基于区域尺度的水稻氮磷钾肥料效应及推荐施肥量研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学博士学位论文, 2014.
Wang W N. Evaluating fertilization effect and fertilizer recommendation of N, Pand K for rice at a regional scale [D]. Wuhan: PhD Dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. |
| [114] |
孙继成, 袁先圣, 董正香, 等. 湖北潜江小麦" 3414”施肥效果评价试验[J].
安徽农学通报, 2011, 17(22): 27–28.
Sun J C, Yuan X S, Dong Z X, et al. Evaluation on fertilization effect of " 3414” wheat in Qianjiang, Hubei province[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 17(22): 27–28. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2011.22.017 |
| [115] |
刘新伟, 龚德平, 巩细民, 等. 湖北江北农场小麦肥效试验与施肥推荐[J].
麦类作物学报, 2012, 32(2): 338–343.
Liu X W, Gong D P, Gong X M, et al. Fertilizer effect on wheat and recommendation of fertilizer for wheat production in Jiangbei Farm[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2012, 32(2): 338–343. DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2012.02.027 |
| [116] |
刘淑军, 秦道珠, 梁海军, 等. 水稻不同基因型品种养分吸收特性[J].
中国农学通报, 2015, 31(3): 16–22.
Liu S J, Qin D Z, Liang H J, et al. Nutrient absorption characteristics of different rice genotype varieties[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(3): 16–22. |
| [117] |
张智, 李小坤, 丛日环, 等. 稻田优化施肥效果与氮、磷环境效益评价[J].
中国农业科学, 2016, 49(5): 906–915.
Zhang Z, Li X K, Cong R H, et al. Optimized fertilization effects and environmental benefits evaluation of nitrogen and phosphorus in the paddy soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(5): 906–915. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.05.010 |
| [118] |
汤雷雷, 万开元, 李祖章, 等. 施肥模式对双季稻产量、养分吸收及经济效益的影响[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(2): 259–268.
Tang L L, Wan K Y, Li Z Z, et al. Effect of fertilizing patterns on grain yield, nutrient uptake and economical efficiency of double-season rice[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(2): 259–268. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2011.0244 |
| [119] |
刘德平, 杨树青, 史海滨, 等. 小麦/玉米套作条件下氮、磷配施的肥料效应研究[J].
中国生态农业学报, 2014, 22(3): 136–142.
Liu D P, Yang S Q, Shi H B, et al. Effect of combined nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer application of wheat-maize intercropping system[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2014, 22(3): 136–142. |
| [120] |
张明. 陕西关中冬小麦/夏玉米轮作体系下合理施肥技术研究[D]. 陕西杨凌: 西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文, 2011.
Zhang M. Research of reasonable fertilizer application technology of winter wheat/summer maize rotation system in Guangzhong area of Shaanxi [D]. Yangling, Shaanxi: MS Thesis of Northwest A&F University, 2011. |
| [121] |
赵营, 周涛, 郭鑫年, 等. 优化施肥对春小麦产量、氮素利用及氮平衡的影响[J].
干旱地区农业研究, 2011, 29(6): 119–124.
Zhao Y, Zhou T, Guo X N, et al. Effect of optimum fertilization on spring wheat yield, N utilization and apparent N balance[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2011, 29(6): 119–124. |
| [122] |
田惠萍. 氮、磷、钾配比施肥对玉米产量的影响[J].
宁夏农林科技, 2013, 54(2): 24–26.
Tian H P. Effect of fertilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on corn yield[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2013, 54(2): 24–26. |
| [123] |
张亚丽. 长期不同施肥对青海小麦产量和土壤钾素的影响[J].
青海大学学报, 2013, 31(6): 69–72.
Zhang Y L. Effects of long-term different fertilization on grain yield and soil K in Qinghai province[J]. Journal of Qinghai University, 2013, 31(6): 69–72. |
| [124] |
徐富贤, 熊洪, 张林, 等. 西南稻区不同地域和施氮水平对杂交中稻氮、磷、钾吸收累积的影响[J].
作物学报, 2011, 37(5): 882–894.
Xu F X, Xiong H, Zhang L, et al. Characteristics of nutrient uptake and utilization of mid-season hybrid rice under different nitrogen application rates in different locations of Southwest China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(5): 882–894. DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2011.05.015 |
| [125] |
刘慧远, 丁永峰. 玉米" 3414”不完全施肥研究[J].
宁夏农林科技, 2012, 53(3): 18–19.
Liu H Y, Ding Y F. Research on corn " 3414” incomplete test[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2012, 53(3): 18–19. |
| [126] |
柴颖, 赵靓, 黄婷, 等. 不同氮、磷配施对春玉米养分吸收和产量的影响[J].
新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(3): 444–449.
Chai Y, Zhao J, Huang T, et al. Effects of different combination ratios of N, P fertilizer on nutrient uptake of maize and yield[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 52(3): 444–449. |
| [127] |
吴向海, 陈淑芳. 彭水县半山区玉米" 3414”肥料试验初报[J].
南方农业, 2012, 6(4): 19–21.
Wu X H, Chen S F. Preliminary report on " 3414” fertilizer experiment in mid-mountain area of Pengshui County[J]. South China Agriculture, 2012, 6(4): 19–21. |
| [128] |
蒋鹏, 熊洪, 朱永川, 等. 施氮量和氮肥运筹模式对糯稻养分吸收积累和氮肥利用率的影响[J].
湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(4): 349–353.
Jiang P, Xiong H, Zhu Y C, et al. Effect of nitrogen rates and nitrogen application patterns on nutrient accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency of glutinous rice[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 42(4): 349–353. |
| [129] |
蒋鹏, 熊洪, 张林, 等. 不同生态条件下施氮量和移栽密度对杂交稻氮、磷、钾吸收积累的影响[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2): 342–350.
Jiang P, Xiong H, Zhang L, et al. Effects of N rate and planting density on nutrient uptake and utilization of hybrid rice under different ecological conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(2): 342–350. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.16280 |
| [130] |
罗永. 四川丘陵区玉米高产高效及最佳养分管理技术研究[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学硕士学位论文, 2011.
Luo Y. Study on high yield and efficiency and the best nutrient management of maize in hill area of Sichuan [D]. Chengdu: MS Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2011. |
| [131] |
王旭, 冯跃华, 李杰, 等. 氮磷钾肥对超级杂交水稻Q优6号干物质积累、养分吸收及产量的影响[J].
中国稻米, 2016, 22(6): 25–29.
Wang X, Feng Y H, Li J, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on dry matter accumulation, nutrient uptake and yield of super hybrid rice Q you 6[J]. China Rice, 2016, 22(6): 25–29. |
| [132] |
黄国斌, 李家贵. 测土配方施肥对玉米养分吸收、产量及效益的影响[J].
贵州农业科学, 2010, 38(1): 23–25.
Huang G B, Li J G. Effects of formulation application on nutrition absorption, yield and benefit of maize[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(1): 23–25. |
| [133] |
邓小强, 邓金池, 汪亮, 等. 氮磷钾配施对杂交玉米禾玉9566农艺性状、产量与养分吸收利用的影响[J].
作物杂志, 2016, (4): 156–161.
Deng X Q, Deng J C, Wang L, et al. Effects of NPK fertilizers combined on agronomic traits, yield, nutrient uptake and utilization of " Heyu 9566” maize[J]. Crops, 2016, (4): 156–161. |
| [134] |
覃金鼓. 杂交玉米肥料利用率试验初报[J].
陕西农业科学, 2016, 62(1): 14–16.
Tan J G. Preliminary report on utilization rate of hybrid maize fertilizer[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 62(1): 14–16. |
| [135] |
李洪文, 苏正飙, 李春莲, 等. 云南紫泥田水稻测土配方施肥试验初报[J].
中国农学通报, 2014, 30(15): 17–23.
Li H W, Su Z B, Li C L, et al. Study on formula application by soil testing of rice in purple paddy field in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(15): 17–23. DOI:10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2013-2469 |
| [136] |
李洪文, 李保华, 李春莲, 等. 紫砂泥田水稻" 3414”肥料效应田间试验[J].
现代农业科技, 2012, (19): 14–16.
Li H W, Li B H, Li C L, et al. Field experiment on fertilizer effect of " 3414” rice in muddy field[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012, (19): 14–16. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2012.19.004 |
| [137] |
刘国一. 西藏一江两河流域农田土壤养分限制因子与小麦氮磷钾最佳施用量研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院硕士学位论文, 2012.
Liu G Y. Study on soil nutrient limiting factors and optimized fertilization rates for winter wheat in main agricultural regions of central Tibet [D]. Beijing: MS Thesis of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012. |
| [138] |
黄东风, 李卫华, 王利民, 等. 水肥管理措施对水稻产量、养分吸收及稻田氮磷流失的影响[J].
水土保持学报, 2013, 27(2): 62–66.
Huang D F, Li W H, Wang L M, et al. Effects of water and fertilizer managements on yield, nutrition uptake of rice and loss of nitrogen and phosphorus by runoff from paddy field[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(2): 62–66. |
| [139] |
李娟, 章明清, 孔庆波, 等. 构建县域早稻氮磷钾施肥的系统聚类方法研究[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2): 531–538.
Li J, Zhang M Q, Kong Q B, et al. Building fertilization categories of N, P and K fertilization for early rice using usystematic clustering method in county territory[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(2): 531–538. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.16123 |
| [140] |
李建国, 刘翠花, 白玛卓玛, 等. 平衡施肥对西藏玉米生物产量及秸秆营养成份的影响[J].
西藏科技, 2013, (9): 3–6.
Li J G, Liu C H, Baima Z M, et al. Effect of balanced fertilization on biomass of corn and straw nutrients in Tibet[J]. Tibet Science and Technology, 2013, (9): 3–6. |
| [141] |
高凡, 张建, 沈建荣, 等. 西双版纳糯玉米 " 3414” 肥效试验研究[J].
农业科技通讯, 2014, (8): 146–149.
Gao F, Zhang J, Shen J R, et al. Experimental study of Xishuangbanna waxy corn fertilizer " 3414”[J]. Yunnan Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014, (8): 146–149. |
| [142] |
何艳琼, 堵文丽, 朱能宏. 氮磷钾肥配施对玉米产量影响的试验研究[J].
云南农业, 2010, (3): 24–25.
He Y Q, Du W L, Zhu N H. Experimental study on the effect of N, P and K fertilizer on maize yield[J]. Yunnan Agriculture, 2010, (3): 24–25. |
| [143] |
章赞德. 闽中丘陵区中稻氮磷钾肥效及其适宜用量研究[J].
福建农业学报, 2016, 31(12): 1294–1298.
Zhang Z D. Effect of NPK fertilization and recommendation for single cropping rice in hilly regions in central Fujian[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 31(12): 1294–1298. |
| [144] |
张桥, 黄旭, 张育灿, 等. 高州市水稻施肥状况分析[J].
广东农业科学, 2012, 39(11): 86–88.
Zhang Q, Huang X, Zhang Y C, et al. Analysis of status in fertilization on rice in Gaozhou[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 39(11): 86–88. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.11.027 |
| [145] |
曾艳, 谢如林, 黄金生, 等. 广西早晚稻氮磷钾锌肥施肥效应[J].
西南农业学报, 2016, 29(4): 831–836.
Zeng Y, Xie R L, Huang J S, et al. Effects of fertilizer application on rice in Guangxi[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 29(4): 831–836. |
| [146] |
徐新朋, 王秀斌, 李大明, 等. 双季稻最佳磷肥和钾肥用量与密度组合研究[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(3): 598–608.
Xu X P, Wang X B, Li D M, et al. Optimum combination of phosphorus, potassium and density for double-rice systems[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(3): 598–608. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.14600 |
| [147] |
张冬明, 王绥干, 吴光辉, 等. 平衡施肥对海南早稻经济性状和产量的影响[J].
湖北农业科学, 2017, 56(9): 1623–1627.
Zhang D M, Wang S G, Wu G H, et al. Effects of balanced fertilization on yield and economic characters of early-season rice[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 56(9): 1623–1627. |
| [148] |
朱文明, 戴勤珍, 吴雄兴, 等. 杂交晚粳" 交源优69”特征特性及高产栽培技术初报[J].
上海农业科技, 2017, (3): 40–42.
Zhu W M, Dai Q Z, Wu X X, et al. Preliminary study on the characteristics and high-yielding cultivation techniques of late japonica hybrid rice[J]. Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, (3): 40–42. |
| [149] |
包红静, 邢月华, 刘艳, 等. 养分专家系统推荐施肥对玉米产量及肥料利用率的影响[J].
辽宁农业科学, 2016, (2): 74–76.
Bao H J, Xing Y H, Liu Y, et al. Nutrition experts recommend fertilization systems on maize yield and fertilizer use efficiency[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2016, (2): 74–76. |
| [150] |
曹立燕. 高产夏玉米群体发育与养分吸收规律研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北农业大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
Cao L Y. Studies on group growth and development and nutrient absorption of high yielding summer maizer [D]. Shijiazhuang: MS Thesis of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2014. |
| [151] |
王艳, 杜永, 陈焕淦, 等. 淮北地区偏大穗型中粳水稻养分吸收特性[J].
耕作与栽培, 2013, (1): 10–12.
Wang Y, Du Y, Chen H G, et al. Nutrient uptake characteristics of large spike-type japonica rice in Huaibei region[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2013, (1): 10–12. |
| [152] |
段敏. 陕西关中地区小麦玉米养分资源管理及其高产探索研究[D]. 陕西杨凌: 西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文, 2010.
Duan M. Study on nutrients management and high yield of wheat and maize in Guanzhong area of Shaanxi province [D]. Yangling, Shaanxi: MS Thesis of Northwest A&F University, 2010. |
| [153] |
曹克莉, 覃金鼓, 蒙正杰, 等. 低产田测土配方施肥对水稻肥料利用率的影响[J].
现代农业科技, 2014, (19): 23–24.
Cao K L, Tan J G, Meng Z J, et al. Effect of fertilization on fertilizer use efficiency of rice fertilizer in low yield field[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014, (19): 23–24. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2014.19.012 |
| [154] |
郭昱. 春播和夏播玉米产量形成特点的研究及适宜品种的筛选[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学硕士学位论文, 2013.
Guo Y. Research about spring and summer sowing maize character of grain yield formation and screening of summer-resistant maize varieties [D]. Chengdu: MS Thesis of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2013. |
| [155] |
熊艳, 王平华, 何晓滨, 等. 云南省水稻土壤养分丰缺指标及肥料利用率研究[J].
西南农业学报, 2012, 25(3): 930–934.
Xiong Y, Wang P H, He X B, et al. Study on soil nutrient rich-lack index and fertilizer using efficiency of rice in Yunnan province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 25(3): 930–934. |
| [156] |
熊艳, 王平华, 何晓滨, 等. 云南省旱地玉米土壤养分丰缺指标及肥料利用率研究[J].
西南农业学报, 2013, 26(1): 203–208.
Xiong Y, Wang P H, He X B, et al. Research on soil nutrient rich-lack index and fertilizer using efficiency of maize in Yunnan province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 26(1): 203–208. |
| [157] |
谢振宇, 沈建凯, 尹明, 等. 不同施肥水平对杂交水稻氮、磷、钾吸收积累的影响[J].
热带农业科学, 2014, 34(9): 1–5.
Xie Z Y, Shen J K, Yin M, et al. Effects of different fertilizer application rates on uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium of hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2014, 34(9): 1–5. |
| [158] |
徐新朋. 基于产量反应和农学效率的水稻和玉米推荐施肥方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院博士学位论文, 2015.
Xu X P. Methodology of fertilizer recommendation based on yield response and agronomic efficiency for rice and maize [D]. Beijing: PhD Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. |
| [159] |
王宜伦, 白由路, 王磊, 等. 基于养分专家系统的小麦–玉米推荐施肥效应研究[J].
中国农业科学, 2015, 48(22): 4483–4492.
Wang Y L, Bai Y L, Wang L, et al. Effects of recommended fertilization based on nutrient expert in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(22): 4483–4492. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2015.22.009 |
| [160] |
孙星, 刘勤, 王德建, 等. 长期秸秆还田对土壤肥力质量的影响[J].
土壤, 2007, 39(5): 782–786.
Sun X, Liu Q, Wang D J, et al. Effect of long-term straw application on soil fertility[J]. Soils, 2007, 39(5): 782–786. |
| [161] |
徐一兰, 唐海明, 肖小平, 等. 长期施肥对双季稻田土壤微生物学特性的影响[J].
生态学报, 2016, 36(18): 5847–5855.
Xu Y L, Tang H M, Xiao X P, et al. Effects of different long-term fertilization regimes on the soil microbiological properties of a paddy field[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(18): 5847–5855. |
| [162] |
张水清, 黄绍敏, 郭斗斗. 主成分分析在潮土土壤肥力评价中的应用[J].
河南农业科学, 2011, 40(4): 82–86.
Zhang S Q, Huang S M, Guo D D. Evaluation of fluvo-aquic soil fertility quality with the method of principal component analyses[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 40(4): 82–86. |
| [163] |
马晓霞, 王莲莲, 黎青慧, 等. 长期施肥对玉米生育期土壤微生物量碳氮及酶活性的影响[J].
生态学报, 2012, 32(17): 5502–5511.
Ma X X, Wang L L, Li Q H, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities during maize growing season[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(17): 5502–5511. |
| [164] |
颜丽, 宋杨, 贺靖, 等. 玉米秸秆还田时间和还田方式对土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J].
土壤通报, 2004, 35(2): 143–148.
Yan L, Song Y, He J, et al. Effects of maize stems returning back to the field on the yield of plants and soil fertility[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004, 35(2): 143–148. |
| [165] |
杜召永. 长期定位施肥对黑土钾素供应能力及玉米品质影响[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
Du Z Y. Effect of long-term fertilization on supply of soil potassium and corn quality [D]. Changchun: MS Thesis of Jilin Agricultural University, 2014. |
| [166] |
邬奇峰, 陆扣萍, 毛霞丽, 等. 长期不同施肥对农田土壤养分与微生物群落结构的影响[J].
中国农学通报, 2015, 31(5): 150–156.
Wu Q F, Lu K P, Mao X L, et al. Responses of soil nutrients and microbial biomass and community composition to long-term fertilization in cultivated land[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(5): 150–156. |
| [167] |
毕于运, 王亚静, 高春雨. 中国主要秸秆资源数量及其区域分布[J].
农机化研究, 2010, 32(3): 1–7.
Bi Y Y, Wang Y J, Gao C Y. Straw resource quantity and its regional distribution in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(3): 1–7. |
| [168] |
谢光辉, 王晓玉, 任兰天. 中国作物秸秆资源评估研究现状[J].
生物工程学报, 2010, 26(7): 855–863.
Xie G H, Wang X Y, Ren L T. China’s crop residues resources evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 26(7): 855–863. |
| [169] |
王亚静, 毕于运, 高春雨. 中国秸秆资源可收集利用量及其适宜性评价[J].
中国农业科学, 2010, 43(9): 1852–1859.
Wang Y J, Bi Y Y, Gao C Y. Collectable amounts and suitability evaluation of straw resource in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(9): 1852–1859. |
| [170] |
曹国良, 张小曳, 郑方成, 等. 中国大陆秸秆露天焚烧的量的估算[J].
资源科学, 2006, 28(1): 9–13.
Cao G L, Zhang X Y, Zheng F C, et al. Estimating the quantity of crop residues burnt in open field in China[J]. Resources Science, 2006, 28(1): 9–13. |
| [171] |
朱建春, 李荣华, 杨香云, 等. 近30年来中国农作物秸秆资源量的时空分布[J].
西北农林科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 2012, 40(4): 139–145.
Zhu J C, Li R H, Yang X Y, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of crop straw resources in 30 years in China[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 139–145. |
| [172] |
汪海波, 秦元萍, 余康. 我国农作物秸秆资源的分布、利用与开发策略[J].
国土与自然资源研究, 2008, (2): 92–93.
Wang H B, Qin Y P, Yu K. Utilization, distribution and exploitation tactics of crop stalk resources in China[J]. Territory Natural Resources Study, 2008, (2): 92–93. |
| [173] |
崔明, 赵立欣, 田宜水, 等. 中国主要农作物秸秆资源能源化利用分析评价[J].
农业工程学报, 2008, 24(12): 291–296.
Cui M, Zhao L X, Tian Y S, et al. Analysis and evaluation on energy utilization of main crop straw resources in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2008, 24(12): 291–296. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.12.060 |
| [174] |
谢光辉, 王晓玉, 韩东倩, 等. 中国非禾谷类大田作物收获指数和秸秆系数[J].
中国农业大学学报, 2011, 16(1): 9–17.
Xie G H, Wang X Y, Han D Q, et al. Harvest index and residue factor of non-cereal crops in China[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2011, 16(1): 9–17. |
| [175] |
王舒娟, 蔡荣. 农户秸秆资源处置行为的经济学分析[J].
中国人口·资源与环境, 2014, 24(8): 162–167.
Wang S J, Cai R. Economic analysis of the straw disposal behavior of farmers[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2014, 24(8): 162–167. |
| [176] |
高祥照, 马文奇, 马常宝, 等. 中国作物秸秆资源利用现状分析[J].
华中农业大学学报 (自然科学版), 2002, 21(3): 242–247.
Gao X Z, Ma W Q, Ma C B, et al. Analysis on the current status of utilization of crop straw in China[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 21(3): 242–247. |
| [177] |
王玄德, 石孝均, 宋光煜. 长期稻草还田对紫色水稻土肥力和生产力的影响[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(3): 302–307.
Wang X D, Shi X J, Song G Y. Effects of long-term rice straw returning on the fertility and productivity of purplish paddy soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(3): 302–307. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2005.0303 |
| [178] |
肖小平, 汤海涛, 纪雄辉. 稻草还田模式对稻田土壤速效氮、钾含量及晚稻生长的影响[J].
作物学报, 2008, 34(8): 1464–1469.
Xiao X P, Tang H T, Ji X H. Effect of patterns of straw returning to field on contents of available N, K in soil and the later rice growth[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(8): 1464–1469. |
| [179] |
油菜秸秆饲用价值分析及其开发利用[J].
内蒙古草业, 2007, 19(1): 41–42.
Wu L, Ma W J, Yi R G L T, et al. Analysis on feeding value of rape straw and its development and utilization[J]. Inner Mongolia Prataculture, 2007, 19(1): 41–42. |
| [180] |
刘芳, 张长生, 陈爱武, 等. 秸秆还田技术研究及应用进展[J].
作物杂志, 2012, (2): 18–23.
Liu F, Zhang C S, Chen A W, et al. Technology research and application prospect of straw returning[J]. Crops, 2012, (2): 18–23. |
| [181] |
李昌明, 王晓玥, 孙波. 不同气候和土壤条件下秸秆腐解过程中养分的释放特征及其影响因素[J].
土壤学报, 2017, 54(5): 1–14.
Li C M, Wang X Y, Sun B. Characteristics of nutrient release and its affecting factors during plant residue decomposition under different climate and soil conditions[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(5): 1–14. |
| [182] |
申源源, 陈宏. 秸秆还田对土壤改良的研究进展[J].
中国农学通报, 2009, 25(19): 291–294.
Shen Y Y, Chen H. The progress of study on soil improvement research with straw stalk[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(19): 291–294. |
| [183] |
王维敏. 麦秸、氮肥与土壤混合培养时氮素的固定、矿化与麦秸的分解[J].
土壤学报, 1986, (2): 97–105.
Wang W M. Immobilization and mineralization of nitrogen and decomposition of straw during incubation of soils mixed with wheat straw and nitrogen fertilizer[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1986, (2): 97–105. |
| [184] |
邱学礼, 郑波, 鲁耀, 等. 玉米秸秆碳氮比调控施用对烟叶氮磷钾吸收的影响[J].
西北农业学报, 2012, 21(8): 125–129.
Qiu X L, Zheng B, Lu Y, et al. Effects of C/N regulated corn straw application on nitrogrn, phosphorus and potassium uptake in tobacco[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2012, 21(8): 125–129. |
| [185] |
王麒, 宋秋来, 冯延江, 等. 施用氮肥对还田水稻秸秆腐解的影响[J].
江苏农业科学, 2017, (11): 197–201.
Wang Q, Song Q L, Feng Y J, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on rice straw decay[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, (11): 197–201. |
| [186] |
张丹, 付斌, 胡万里, 等. 秸秆还田提高水稻-油菜轮作土壤固氮能力及作物产量[J].
农业工程学报, 2017, (9): 133–140.
Zhang D, Fu B, Hu W L, et al. Increasing soil nitrogen fixation capacity and crop yield of rice-rape rotation by straw returning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, (9): 133–140. DOI:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.017 |
| [187] |
马琳, 张卫华, 刘淼. 不同水氮条件下小麦和玉米秸秆养分释放特征研究[J].
西部大开发(土地开发工程研究), 2017, (2): 57–62.
Ma L, Zhang W H, Liu M. Wheat and corn straw nutrient release characteristics of different water and nitrogen conditions[J]. Land Development and Engineering Research, 2017, (2): 57–62. |
| [188] |
戴志刚, 鲁剑巍, 李小坤, 等. 不同作物还田秸秆的养分释放特征试验[J].
农业工程学报, 2010, 26(6): 272–276.
Dai Z G, Lu J W, Li X R, et al. Nutrient release characteristic of different crop straws manure[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(6): 272–276. |
| [189] | Choudhury A T M A, Kennedy I R. Prospects and potentials for systems of biological nitrogen fixation in sustainable rice production[J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 2004, 39(4): 219–227. |
| [190] | Cong P T, Dung T D, Hien T M, et al. Inoculant plant growth-promoting microorganisms enhance utilisation of urea-N and grain yield of paddy rice in southern Vietnam[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2009, 45(1): 52–61. DOI:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2008.06.006 |
| [191] |
丁文成, 李书田, 黄绍敏. 氮肥管理和秸秆腐熟剂对15N标记玉米秸秆氮有效性与去向的影响
[J].
中国农业科学, 2016, 49(14): 2725–2736.
Ding W C, Li S T, Huang S M. Bioavailability and fate of nitrogen from 15N-labeled corn straw as affected by nitrogen management and straw microbial inoculants [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(14): 2725–2736. DOI:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.14.007 |
| [192] |
单鹤翔, 卢昌艾, 张金涛, 等. 不同肥力土壤下施氮与玉米秸秆还田对冬小麦氮素吸收利用的影响[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(1): 35–41.
Shan H X, Lu C A, Zhang J T, et al. Effect of maize straw applied with N fertilizer on nitrogen adsorption of winter wheat under different soil fertility[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(1): 35–41. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2012.11227 |
| [193] | Laberge G, Ambus P, Hauggaardnielsen H, et al. Stabilization and plant uptake of N from 15N-labelled pea residue 16.5 years after incorporation in soil [J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2006, 38(7): 1998–2000. |
| [194] | Haynes R J. Fate and recovery of 15N derived from grass/clover residues when incorporated into a soil and cropped with spring or winter wheat for two succeeding seasons [J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 1997, 25(2): 130–135. |
| [195] |
朱兆良. 氮素管理与粮食生产和环境[J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(增刊): 3–11.
Zhu Z L. Nitrogen management in relation to food production and environment in China [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002, 39(Supplement): 3–11. |
| [196] |
陈冬林, 易镇邪, 周文新, 等. 不同土壤耕作方式下秸秆还田量对晚稻土壤养分与微生物的影响[J].
环境科学学报, 2010, 30(8): 1722–1728.
Chen D L, Yi Z X, Zhou W X, et al. Effects of straw return on soil nutrients and microorganisms in late rice under different soil tillage systems[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(8): 1722–1728. |
| [197] |
钱凤魁, 黄毅, 董婷婷, 等. 不同秸秆还田量对旱地土壤水肥和玉米生长与产量的影响[J].
干旱地区农业研究, 2014, (2): 61–65.
Qian F K, Huang Y, Dong T T, et al. Effect of crop residue incorporation on soil moisture and nutrient and maize growth and yield of arid farmland[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2014, (2): 61–65. DOI:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2014.02.010 |
| [198] |
徐国伟, 翟志华, 陈珂, 等. 不同秸秆还田量对直播水稻生长特性的影响[J].
广东农业科学, 2015, 42(16): 1–6.
Xu G W, Zhai Z H, Chen K, et al. Effects of different amounts of wheat-residue application on growth of direct-seeding rice[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(16): 1–6. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.16.001 |
| [199] |
韩新忠, 朱利群, 杨敏芳, 等. 不同小麦秸秆还田量对水稻生长、土壤微生物生物量及酶活性的影响[J].
农业环境科学学报, 2012, (11): 2192–2199.
Han X Z, Zhu L Q, Yang M F, et al. Effects of different amount of wheat straw returning on rice growth, soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, (11): 2192–2199. |
| [200] |
张静, 温晓霞, 廖允成, 等. 不同玉米秸秆还田量对土壤肥力及冬小麦产量的影响[J].
植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 612–619.
Zhang J, Wen X X, Liao Y C, et al. Effects of different amount of maize straw returning on soil fertility and yield of winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(3): 612–619. DOI:10.11674/zwyf.2010.0314 |
| [201] |
杨滨娟, 黄国勤, 徐宁, 钱海燕. 秸秆还田配施不同比例化肥对晚稻产量及土壤养分的影响[J].
生态学报, 2014, 34(13): 3779–3787.
Yang B J, Huang G Q, Xu N, Qian H Y. The effects of returning straw containing fertilizer with varying nutrient ratios on rice yield and soil fertility[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(13): 3779–3787. |
| [202] |
杨滨娟, 黄国勤, 钱海燕, 等. 秸秆还田对稻田生态系统环境质量影响的初步研究[J].
中国农学通报, 2012, 28(2): 200–208.
Yang B J, Huang G Q, Qian H Y, et al. The preliminary research about the influence of rice-straw returning on the rice ecosystem environment quality[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(2): 200–208. DOI:10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2011-1755 |
 2018, Vol. 24
2018, Vol. 24  doi:
doi: 

