2. 西南石油大学 地球科学与技术学院, 四川 成都 610500
2. School of Geoscience and Technology, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu 610500, China
四川盆地中震旦系灯影组丘滩相白云岩储层是近年来深层—超深层碳酸盐岩储层研究的热点。不同学者对丘滩体发育的主控因素、成因模式进行研究,部分学者还对丘滩的层序地层进行了研究[1],甚至有学者利用三维建模与地震正演技术对丘滩体进行了结构研究[2],发现走滑断层对丘滩分布的多样性也具有一定影响[3]。
继20世纪60年代在四川盆地发现威远震旦系灯影组气田以来,2011年在川中古隆起灯影组二段(简称灯二段)获得高产工业气(GS1井日产天然气102.15×104 m3)[4-5]。近年来,为拓宽勘探领域,跳出古隆起限制,增加实际生产开采,于2020年和2021年在古隆起北斜坡蓬莱—中江地区针对灯二段气藏分别部署了PT1井和PT101井,均获得高产气流(PT1井测试日产气121.98×104 m3,PT101井测试日产气220.88×104 m3),实现了四川盆地灯影组气藏勘探新的突破,证实了蓬莱—中江地区灯二段气藏具有较好的勘探开发潜力[6-10]。以往关于蓬莱—中江地区灯二段气藏的研究主要聚焦于沉积环境、储层特征、气藏特征、封盖有效性等方面,认为四川盆地震旦系灯影组丘滩白云岩储层存在巨大的天然气勘探潜力,储层发育受控于沉积相、岩溶、埋藏-热液等因素[11-14],并证实了蓬莱—中江地区灯二段存在构造-岩性圈闭气藏[15],但由于灯二段具有气藏埋藏深度大、勘探难度大,尤其限于以往钻井较少、分析化验资料不足等客观条件,对于蓬莱—中江地区灯二段气藏特征等认识还有待进一步深化。鉴于此,随着勘探的不断深入,在以往的研究基础上,依托新增钻井、岩心、铸体薄片、地震和分析化验资料,对蓬莱—中江地区灯二段气藏沉积相、储集条件、烃源条件、封盖条件等进行分析,并进一步对成藏条件与成藏模式进行研究,以期为继续深化蓬莱—中江地区灯二段气藏认识及后续勘探开发提供地质依据。
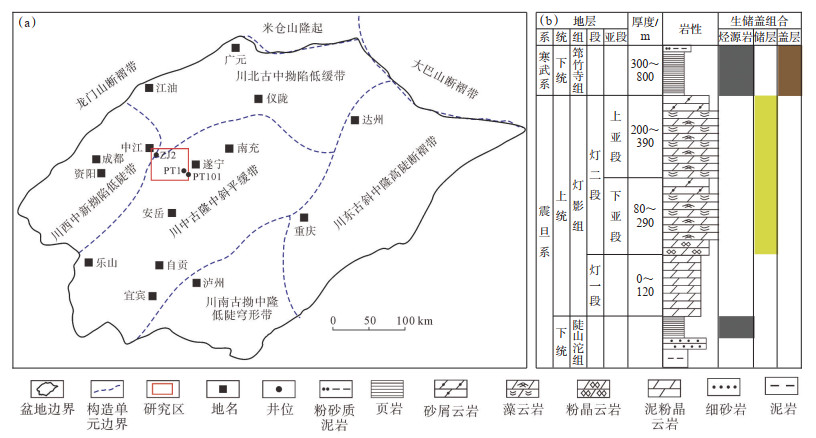
1 地质概况蓬莱—中江地区构造上位于川中古隆中斜平缓带北部、德阳—安岳古裂陷槽东侧,东达遂宁市,西抵中江县[16],勘探面积约0.3×104 km2(图 1a)。四川盆地震旦系灯影组可分为4个岩性段(灯一段—灯四段),由于上扬子区域震旦系灯影组沉积后受桐湾期构造抬升运动的影响[17],研究区灯影组仅保留了灯一段和灯二段,与下伏陡山坨组呈整合接触,与上覆寒武系筇竹寺组呈不整合接触(图 1b)[18]。其中灯二上亚段在PS3井、PS4井区已被剥蚀,在PT101-ZJ2井区保存较全,地层厚度为200~390 m,岩性以藻云岩、砂屑云岩和粉晶云岩为主,可与上覆寒武系筇竹寺组暗色页岩组成“上生下储上盖”和“旁生侧储上盖”的生-储-盖配置关系。PT101-ZJ2井区灯二下亚段以产水为主,因此,本次重点针对灯二段上亚段开展研究。
|
下载原图 图 1 四川盆地中部北斜坡构造位置(a)及震旦系灯影组岩性地层综合柱状图(b) Fig. 1 Structural location of the northern slope(a)and stratigraphic colunm of Sinian Dengying Formation(b)in central Sichuan Basin |
由于南沱冰期冰川消融,四川盆地震旦系陡山沱组沉积期以古陆供给物源的潮坪和滨岸沉积格局为主[19],岩性主要为浅黑色泥岩、深灰色泥质砂岩和黑灰色页岩等。随着海水侵入,灯影组沉积期古陆多被淹没或侵蚀夷平,盆地内逐渐演变为碳酸盐岩台地[20]。灯二上亚段沉积期,川中北斜坡以发育台地边缘滩相和台地边缘丘相为特色,并可分为滩核、滩缘、滩间海、丘核、丘缘、丘间海6种亚相,又可进一步分为云质滩/丘核、云质滩/丘缘和云质滩/丘间海多种微相(表 1)。
|
|
下载CSV 表 1 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段沉积相划分 Table 1 Sedimentary facies division of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
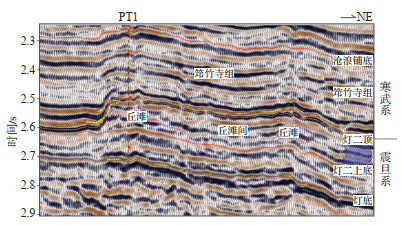
根据颗粒岩累积厚度/地层厚度值的差异,将台地边缘丘/滩划分为丘/滩核(颗粒岩累积厚度/地层厚度值大于0.6)、丘/滩缘(颗粒岩累积厚度/地层厚度值为0.4~0.6)以及丘/滩间海(颗粒岩累积厚度/地层厚度值小于0.4)3种亚相。丘/滩核、丘/滩缘亚相岩性主要包括菌藻类作用形成的浅褐色—深褐色富藻白云岩、浅褐灰色砂屑云岩(可见砾屑、鲕粒等)与白灰色粉晶云岩,地震剖面上具有明显的丘状外形结构,发育区整体呈中弱断续变振幅特征,内部呈断续蚯蚓状反射。丘/滩间海在地震剖面上则表现为席状平行强反射特征(图 2),主要发育云质丘/滩间海微相,岩性为浅灰色泥(粉)晶云岩,由于台地边缘丘和台地边缘滩形成于台地边缘高能相带,水动力强,单丘体和单滩体均较厚,在成岩演化过程中有利于储层发育。
|
下载原图 图 2 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯影组地震剖面 Fig. 2 Seismic section of Sinian Dengying Formation in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
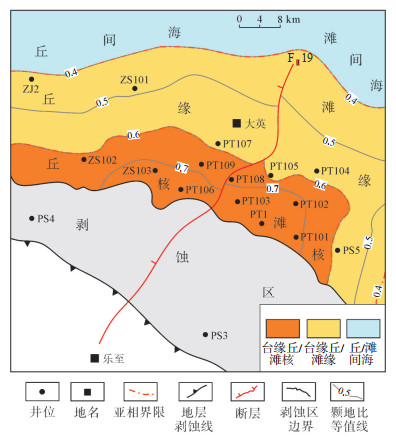
根据单井颗粒岩累积厚度/地层厚度值,采用优势相编图方法,编绘了蓬莱—中江地区灯二上亚段沉积相平面分布图(图 3)。从图 3中可见,研究区灯二上亚段发育台地边缘丘/滩,由于走滑断层FⅡ19(断距约100.0 m,延伸长度为45.9 km,断开二叠系—前震旦)的影响,台缘丘/滩主体分为东、西2个部分。丘/滩核亚相主要位于东侧的PT108井—PT103井—PT1井—PT101井一带和西侧的PT109井—PT106井—ZS102井一带,丘/滩核外缘为丘/滩缘亚相,分别位于FⅡ19断层东侧的PT104井—PS5井和西侧的ZJ2井—ZS101井区域,丘/滩缘以外发育丘/滩间海。
|
下载原图 图 3 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段沉积相平面分布 Fig. 3 Distribution of sedimentary facies of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
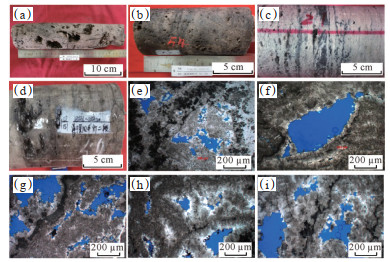
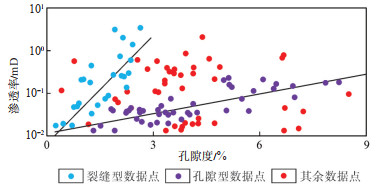
四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段储层的储集岩类以藻云岩、藻砂屑云岩为主(图 4),其中发育各种溶蚀孔洞,主要包括溶洞(图 4a)、粒间溶孔(图 4e)和粒内溶孔(图 4h)。灯二上亚段岩心的孔渗关系结果表明,孔渗样品点分散,相关性中等—较差,孔隙度为2%~5%,分布频率大于85%,渗透率为0.01 mD~1.00 mD,分布频率大于90%(图 5)。孔隙度小于3% 的部分样品受裂缝改造呈“低孔中渗”特征,可能是由于钻样过程中产生的裂缝和地层开启后应力释放产生的裂缝所致;孔隙度大于3% 的样品既存在具有孔渗呈正相关的样品点,又存在渗透率较低(均小于1.00 mD),表现为“中孔低渗”孤立孔隙特征的样品点(图 5)。结合储层岩石学特征和孔渗关系分析,认为研究区灯二上亚段存在4种类型的储层:①随孔隙度增大,渗透率缓慢增加的残余粒间孔+粒间溶孔型储层;②表现为“中孔低渗”孤立孔隙特征的粒内溶孔+藻格架孔型储层;③裂缝改造“低孔中渗”特征的裂缝型储层;④非组构选择性溶蚀形成的孔洞型储层。
|
下载原图 图 4 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段典型岩石学特征 (a)浅褐色藻云岩,溶蚀孔洞,PT101井,5 774.87~5 775.19 m;(b)深褐色藻云岩,溶蚀孔洞,PT101井,5 738.98~5 739.15 m;(c)浅褐灰色含藻砂屑云岩,沥青充填,ZJ2井,6 556.06~6 556.19 m;(d)浅褐色藻砂屑云岩,溶蚀孔洞,PT103井,5 722.42~5 722.68 m;(e)藻云岩,粒内溶孔、粒间溶孔,PT101井,5 773.36 m;(f)藻叠层云岩,溶蚀孔洞,PT101井,5 741.88 m,铸体;(g)藻云岩,粒内溶孔、残余粒间孔,PT101井,5 737.08 m,铸体;(h)藻云岩,粒内溶孔为主,PT101井,5 739.16 m,铸体;(i)藻云岩,粒内溶孔为主,可见粒间溶孔,PT1井,5 841.23 m,铸体。 Fig. 4 Typical petrological characteristics of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
|
下载原图 图 5 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段岩心孔渗交会图 Fig. 5 Cross plot of core porosity and permeability of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
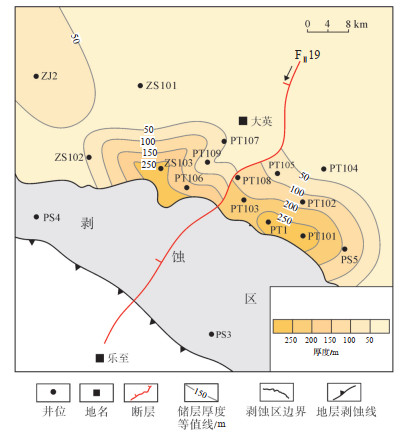
四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段储层厚度分布特征与沉积相分布特征较吻合,储层累积厚度高值区主要位于台缘丘/滩核内,呈“东厚西薄、南厚北薄”的平面分布(图 6),高值区主要位于FⅡ19断层东侧PT1井—PT101井区和FⅡ19断层西侧ZS103井区,储层累积厚度均大于200 m。向PT1井—PT101井区高值区外缘,储层累积厚度逐渐减小,为20~180 m,ZS103井高值区外缘,储层累积厚度逐渐减小,为60~170 m,ZJ2井、ZS101井储层累积厚度分别为142 m和69 m。
|
下载原图 图 6 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段储层厚度平面分布 Fig. 6 Distribution of reservoir thickness of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
四川盆地寒武系烃源岩发育,而筇竹寺组泥页岩更是高有机质丰度的烃源岩[21]。对多口实钻探井进行分析化验得出,古隆起北斜坡发育大范围筇竹寺组烃源岩,TOC为2.5%,干酪根显微组分主要为腐泥型,属于Ⅰ型干酪根。研究区灯影组碳同位素数据分析结果显示,灯影组的ln(C1/C2)值为7~8,ln(C2/C3)值为3~5,Ro为2.0%~2.5%,表明研究区灯影组烃源演化程度较高。以往研究已证实该区灯二段气藏属于筇竹寺组烃源岩提供的原油裂解气[22]。
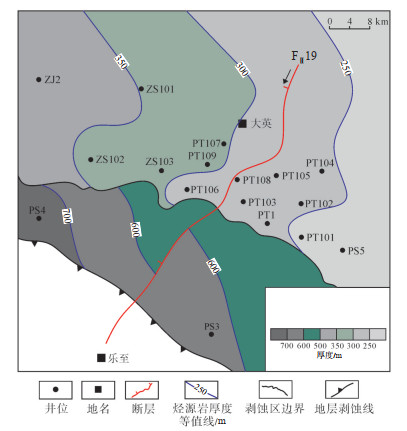
四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度具有“西厚东薄”的分布特征,高值区位于PS4井区,厚度大于700 m,低值区主要位于PS5井区,厚度小于250 m,PT104井—PT108井—PT101井区厚度为200~300 m,ZS101井—ZS103井区厚度为300~350 m(图 7),表明研究区灯二上亚段气藏具备较好的烃源条件。
|
下载原图 图 7 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区寒武系筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度平面分布 Fig. 7 Distribution of source rock thickness of Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
直接盖层是气藏保存的重要条件[23],区域盖层可为形成有利的成藏组合及气藏保存提供重要保障[24]。蓬莱—中江地区下寒武统筇竹寺组泥页岩是灯二上亚段气藏重要的区域性盖层,泥页岩厚度为200~750 m,孔隙度小于2%,渗透率小于0.015 mD,低孔低渗条件使其突破压力为16~50 MPa,自筇竹寺组烃源岩生烃高峰期开始即已具备封盖能力。川中古隆起筇竹寺组泥页岩在喜山构造期未抬升至破裂深度,仍对下伏灯二段气藏具有封闭能力[25],有利于气藏的保存。此外,横向上区内台地边缘丘/滩-丘/滩间海的沉积组合特征造就了丘/滩间致密泥晶云岩形成岩性遮挡,形成了良好的封堵条件。
4.1.3 生-储-盖组合蓬莱—中江地区筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度大,具有较高的有机质成熟度和生气强度,气源充足。在台地边缘丘滩与溶蚀作用的共同作用下[26],灯二上亚段形成孔、洞、缝广泛发育的叠置连片优质储层。受桐湾运动一期影响,灯二段顶面的区域不整合面和大量断裂体系为研究区气藏形成提供了优质的储集空间和运移通道。筇竹寺组发育大范围的厚层致密泥页岩,可作为为灯二上亚段气藏的优质封盖层。因此,认为研究区灯二上亚段气藏具有“上生下储上盖”和“旁生侧储上盖”2种较好的生-储- 盖配置关系。
根据PS3井—PT1井—PT104井生-储-盖配置连井对比剖面(图 8)与PS4井—ZS103井—PT109井—PT107井生-储-盖配置连井对比剖面(图 9)可以看出,PT101所在井区和ZS103所在井区充注基本一致,但受FⅡ19断层影响,2个井区气水界面存在差异。PT101井区和ZS103井区为“侧生旁储”充注型,属“旁生侧储上盖”模式,而研究区北部ZJ2井、ZS101井充注不一致,表明不同的运聚方式导致区内灯二上亚段气藏的充注存在差异,为“上生下储”充注型,属“上生下储上盖”模式。
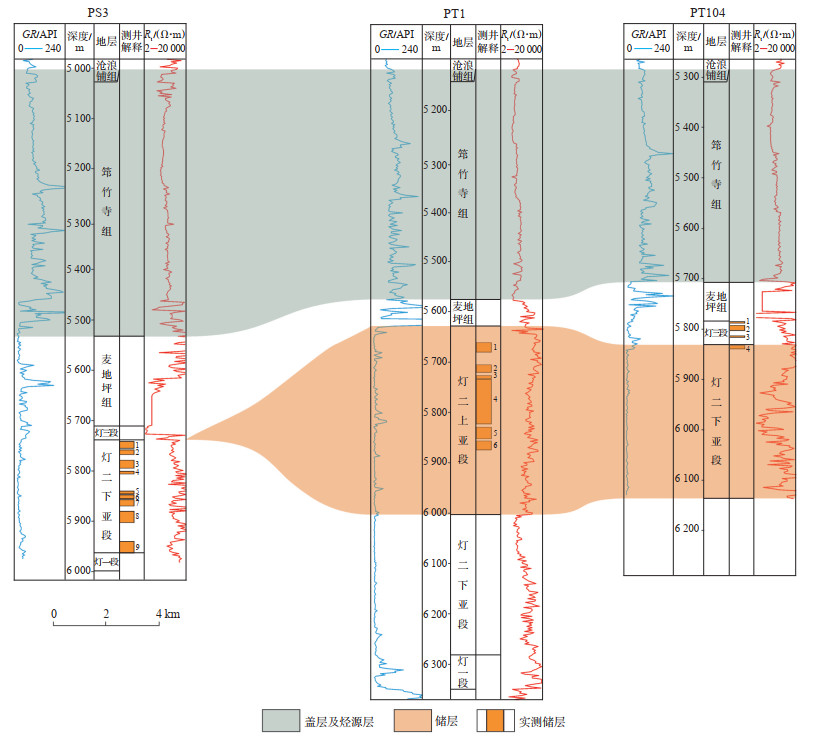
|
下载原图 图 8 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区PS3井—PT1井—PT104井生-储-盖配置连井对比剖面 Fig. 8 Well-tie profile of source-reservoir-cap assemblage across wells PS3, PT1 and PT104 in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
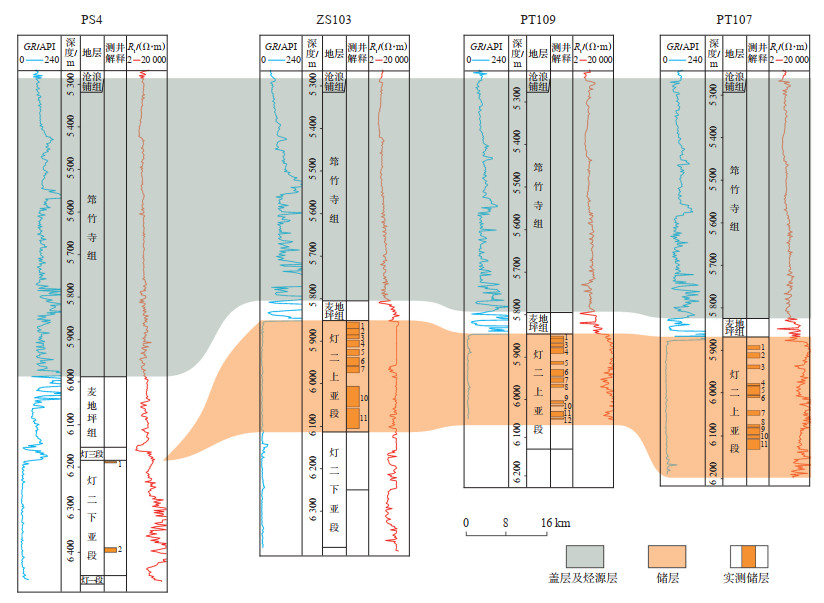
|
下载原图 图 9 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区PS4井—ZS103井—PT109井—PT107井生-储-盖配置连井对比剖面 Fig. 9 Well-tie profile of source-reservoir-cap assemblage across wells PS4, ZS103, PT109 and PT107 in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
根据上述研究,研究区以灯二上亚段为储集层、筇竹寺组泥页岩为烃源层、筇竹寺组顶部为盖层的生-储-盖配置关系,以FⅡ19断层封堵、各级小断裂为断层输导,使研究区出现了现今的储集格局。
4.2 成藏模式研究区油气主要充注于三叠纪—白垩纪,为多期“准连续”型。以PT1井为例,寒武系筇竹寺组烃源岩处于未成熟阶段,而震旦系烃源岩已进入生油期;由于构造抬升作用,二叠纪前生烃过程停止;二叠纪—三叠纪,烃源岩进入生油高峰期;早侏罗世,烃源岩进入成熟—高成熟湿气生成期;晚侏罗世—白垩纪,烃源岩处于干气生成期;白垩纪末之后,由于地层抬升,气藏逐渐调整最终定型。寒武系的龙王庙组、二叠系油气主要在晚三叠世—中侏罗世与早—中侏罗世充注。
进一步分析可解释为研究区灯二上亚段气藏先后经历了奥陶纪—志留纪古油气藏聚集、志留纪—石炭纪古油藏破坏、二叠纪—三叠纪再次生烃成油藏和三叠纪—侏罗纪原油裂解生气4个阶段(图 10)。加里东运动时期,地层虽存在抬升剥蚀,但总体上仍以沉积压实为主;海西运动时期,构造抬升,埋藏作用减弱;印支运动时期,遭受轻微抬升侵蚀作用,沉积物持续沉降;进入燕山运动晚期之后,地层逐渐抬升并接受剥蚀,埋藏作用明显减弱。
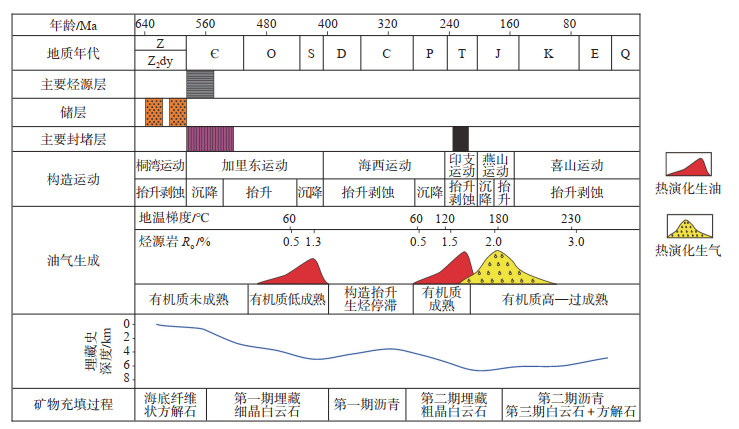
|
下载原图 图 10 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段气藏埋藏模式示意图 Fig. 10 Gas reservoir burial model of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
油气生成在奥陶纪晚期以热演化生油为主,烃源岩Ro高峰值达1.3%;至二叠纪再次生烃并从热演化生油向热演化生气转化,Ro峰值接近3.0%。天然气藏的形成分别经历了古油藏—古气藏的演化过程。研究区灯二上亚段藻丘和台缘滩体在岩溶作用下形成溶蚀孔洞型储层。在圈闭形成过程中,由于构造的影响,逐渐形成西部低、东部高的岩性圈闭。
随着演化程度加强,震旦系沉积晚期第1期盐水充注至储层当中;加里东构造沉降时,在断裂输导体系作用下,筇竹寺组烃源岩生成烃类运移后形成古油藏,构成“上生下储上盖”模式。在海西运动的构造抬升作用影响下,古油藏遭受破坏,第2期盐水充注;二叠系沉积期,上覆烃源层中液态油持续生烃;至三叠系沉积前,第3期油气充注,筇竹寺组底部烃源岩生成的烃类侧向运移至灯二上亚段储层中,上覆丘滩间的致密层和筇竹寺组盖层对储层中的烃类联合封堵,形成大型岩性油藏,构成“旁生侧储上盖”模式(图 11)。
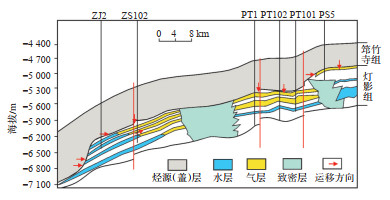
|
下载原图 图 11 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段气藏成藏模式示意图 Fig. 11 Gas reservoir accumulation model of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
进入侏罗纪,烃源岩有机质处于高成熟阶段,古油藏逐渐聚集轻质原油和湿气。晚侏罗世之后,第3期天然气充注,聚集的液态烃以及部分重烃气体进一步裂解,气样分析显示出研究区气藏中存有古油藏各阶段的裂解气。
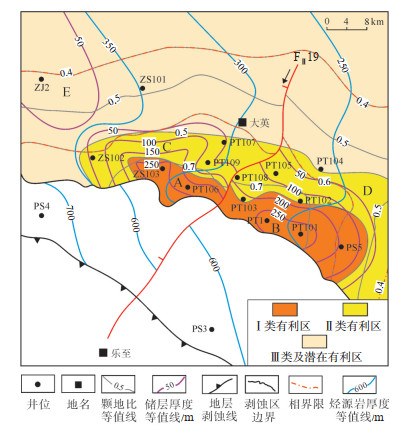
4.3 有利勘探区以沉积相平面展布、有效烃源岩分布、储层分布3个主控因素作为勘探区评价条件,结合试气成果以及成藏模式,划分出Ⅰ类、Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类等3个有利区带(5个有利区块),分布于FⅡ19断层两侧(图 12、表 2)。
|
下载原图 图 12 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段储层有利区块预测 Fig. 12 Favorable block prediction of reservoir of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
|
|
下载CSV 表 2 四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段有利区块评价 Table 2 Evaluation of favorable block of the upper Sinian Deng-2 member in Penglai-Zhongjiang area, Sichuan Basin |
Ⅰ类有利区为ZS103井—PT106井—PT1井—PT101井—PS5井区,该区处于台缘丘/滩核的有利沉积相带,储层厚度大于100 m,筇竹寺组盖层厚度大于250 m,侧向与烃源岩直接接触,以“旁生侧储上盖”为主,测井解释气层累积厚度大于60 m,PT1井、PT101井、PT106井、ZS103井测试均获得高产,分别为121.98×104 m3/d,220.88×104 m3/d,85.01× 104 m3/d和120.88×104 m3/d。
Ⅱ类有利区为ZS102井—PT109井—PT108井—PT104井区,ZS102井区主要处于台缘丘/滩缘的有利沉积相带,储层厚度大于50 m,筇竹寺组盖层厚度大于200 m,与Ⅰ类有利区接触,以“旁生侧储上盖”为主,但距离陡坎带较远,成藏效率有所降低,测试产量多为20×104 m3/d。
Ⅲ类有利区为ZJ2井区,处于台缘丘/滩的沉积相带,储层厚度大于50 m,筇竹寺组盖层厚度大于350 m,以“上生下储上盖”为主,成藏效率不高,气柱高度有限,测试产量多小于10×104 m3/d。
5 结论(1)四川盆地蓬莱—中江地区震旦系灯二上亚段沉积期发育台地边缘丘和台地边缘滩相,可分为丘/滩核、丘/滩缘与丘/滩间海6种亚相,又可进一步分为云质丘/滩核、云质丘/滩缘与云质丘/滩间海多种微相。
(2)研究区灯二上亚段储层的储集岩类以藻云岩、藻砂屑云岩为主,储集岩发育各种溶蚀孔洞,存在残余粒间孔+粒间溶孔型、粒内溶孔+藻格架孔型、裂缝型储层与孔洞型4种类型的储层,位于台地边缘丘/滩核的储层累积厚度大于50 m,平均储层累积厚度为183 m,具备气藏有利储层条件。
(3)研究区灯二上亚段气藏具备较好的烃源条件和封盖条件,具有“上生下储上盖”和“旁生侧储上盖”2种较好的生-储-盖配置关系。气藏主要经历了奥陶纪—志留纪古油气藏聚集阶段、志留纪—石炭纪古油藏破坏阶段、二叠纪—三叠纪再次生烃成油藏阶段和三叠纪—侏罗纪原油裂解生气阶段。
(4)FⅡ19断层以东的PT101井区和以西的ZS103井区为Ⅰ类有利区块,属“旁生侧储上盖”的成藏模式,其周缘带为Ⅱ类有利区块,而ZJ2井区为Ⅲ类有利区块,属“上生下储上盖”的成藏模式。
| [1] |
HU Mingyi, GAO Da, WEI Guoqi, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and facies architecture of a moundshoaldominated dolomite reservoir in the late Ediacaran Dengying Formation, central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(3): 1653-1671. DOI:10.1002/gj.3261 |
| [2] |
XIONG Ran, ZHENG Jianfeng, WANG Xinxin, et al. 3D out crop geologic modeling and seismic forward modeling of moundbeach complexes. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2022, 15(14): 1-12. |
| [3] |
WEN Long, RAN Qi, TIAN Weizhen, et al. Strike-slip fault effects on diversity of the ediacaran mound-shoal distribution in the central sichuan intracratonic Basin, China. Energies, 2022, 15: 5910. DOI:10.3390/en15165910 |
| [4] |
谢增业, 李剑, 杨春龙, 等. 川中古隆起震旦系-寒武系天然气地球化学特征与太和气区的勘探潜力. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(7): 1-14. XIE Zengye, LI Jian, YANG Chunlong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Sinian-Cambrian natural gas in central Sichuan paleo-uplift and exploration potential of Taihe gas area. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(7): 1-14. DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.07.001 |
| [5] |
魏国齐, 谢增业, 杨雨, 等. 四川盆地中部北斜坡震旦系-寒武系大型岩性气藏形成条件. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(5): 835-846. WEI Guoqi, XIE Zengye, YANG Yu, et al. Formation conditions of Sinian-Cambrian large lithologic gas reservoirs in the north slope area of central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(5): 835-846. |
| [6] |
耿夏童, 邢凤存, 闫海军, 等. 四川盆地磨溪地区震旦系灯影组四段储层特征及勘探启示. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(6): 126-140. GENG Xiatong, XING Fengcun, YAN Haijun, et al. Reservoir characteristics of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation and its implications for oil and gas exploration in Moxi area, Sichuan Basin. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(6): 126-140. |
| [7] |
周红飞, 戴鑫, 贾敏, 等. 川中古隆起北斜坡震旦系灯影组二段油气成藏特征. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(5): 130-138. ZHOU Hongfei, DAI Xin, JIA Min, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(5): 130-138. |
| [8] |
WU Juan, LIU Shugen, WANG Guozhi, et al. Multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulation and formation pressure evolution in Sinian Dengying Formation-Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation, Gaoshiti-Moxi structure, Sichuan Basin. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 27(5): 835-845. DOI:10.1007/s12583-016-0706-4 |
| [9] |
XU Fanghao, XU Guosheng, YUAN Haifeng, et al. Fluid system and pressure evolution study based on isotope and fluid inclusion geochemistry: A case study on the Sinian Dengying and the Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation in the Gaoshiti-Moxi structure, central Sichuan Basin. Arabian journal of geosciences, 2019, 12(8): 260. DOI:10.1007/s12517-019-4315-2 |
| [10] |
任佳鑫, 宋金民, 刘树根, 等. 四川盆地灯影组二段微生物丘滩体结构类型与沉积模式. 石油学报, 2023, 44(2): 312-328. REN Jiaxin, SONG Jinmin, LIU Shugen, et al. Framework and sedimentary model of microbial mound-bank complex in member 2 of Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(2): 312-328. |
| [11] |
杨雨, 文龙, 宋泽章, 等. 川中古隆起北部蓬莱气区多层系天然气勘探突破与潜力. 石油学报, 2022, 43(10): 1351-1368. YANG Yu, WEN Long, SONG Zezhang, et al. Breakthrough and potential of natural gas exploration in multi-layer system of Penglai gas area in the north of central Sichuan paleo-uplift. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(10): 1351-1368. |
| [12] |
谢继容, 张自力, 钟原, 等. 四川盆地中部-北部地区灯影组二段天然气勘探新认识及潜力分析. 海相油气地质, 2022, 27(3): 225-235. XIE Jirong, ZHANG Zili, ZHONG Yuan, et al. New understanding and potential analysis of natural gas exploration of the Dengying member 2 in central-northern area of Sichuan Basin. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2022, 27(3): 225-235. |
| [13] |
王亮, 苏树特, 马梓柯, 等. 川中地区寒武系沧浪铺组沉积特征. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(6): 19-31. WANG Liang, SU Shute, MA Zike, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of Cambrian Canglangpu Formation in central Sichuan Basin. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(6): 19-31. |
| [14] |
CHE Zhenqiang, TAN Xiucheng, DENG Jiating, et al. The characteristics and controlling factors of facies-controlled coastal eogenetic karst: Insights from the fourth member of Neoproterozoic Dengying Formation, central Sichuan Basin, China. Carbonates & Evaporites, 2019, 34(4): 1771-1783. |
| [15] |
范俊佳, 姜华, 鲁雪松, 等. 四川盆地蓬莱地区震旦系灯影组气藏压力演化与成藏过程. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(12): 32-43. FAN Junjia, JIANG Hua, LU Xuesong, et al. Pressure evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation process of Sinian Dengying Formation gas reservoirs in the Penglai area, Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(12): 32-43. |
| [16] |
刘朱睿鸷, 胡素云, 谷志东, 等. 川西震旦系台内坳槽西缘地层划分与沉积演化. 海相油气地质, 2022, 27(4): 360-370. LIUZHU Ruizhi, HU Suyun, GU Zhidong, et al. The stratigraphic division and sedimentary evolution of the western Sinian intraplatform trough in the western Sichuan Basin, South China. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2022, 27(4): 360-370. |
| [17] |
马奎, 文龙, 张本健, 等. 四川盆地德阳-安岳侵蚀裂陷槽分段性演化分析和油气勘探意义. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(2): 274-284. MA Kui, WEN Long, ZHANG Benjian, et al. Segmented evolution of Deyang-Anyue erosion rift trough in Sichuan Basin and its significance for oil and gas exploration, SW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(2): 274-284. |
| [18] |
DING Xiong, TAN Xiucheng, LI Ling, et al. Differences between the platform-margin shoal reservoirs and the platform-interior shoal reservoirs of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Sichuan Basin, China. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2014, 29(4): 349-361. DOI:10.1007/s13146-014-0213-6 |
| [19] |
张玺华, 李勇, 张本健, 等. 四川盆地中江-蓬莱地区灯二段储层特征及优质储层成因机制. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(3): 301-312. ZHANG Xihua, LI Yong, ZHANG Benjian, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of high quality reservoir of the second member of the Dengying Formation in Zhongjiang-Penglai area, Sichuan Basin, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2023, 50(3): 301-312. |
| [20] |
李剑, 杨春龙, 谢武仁, 等. 四川盆地安岳气田震旦系台缘带和台内地区天然气成藏差异性及勘探领域. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(1): 34-45. LI Jian, YANG Chunlong, XIE Wuren, et al. Differences of natural gas accumulation and play fairways in the marginal zone and interior of Sinian platform in Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(1): 34-45. |
| [21] |
付小东, 陈娅娜, 罗冰, 等. 中上扬子区下寒武统麦地坪组-筇竹寺组烃源岩与含油气系统评价. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(4): 103-120. FU Xiaodong, CHEN Ya'na, LUO Bing, et al. Evaluation of source rocks and petroleum system of the Lower Cambrian Maidiping Formation-Qiongzhusi Formation in the Middle-Upper Yangtze region. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(4): 103-120. |
| [22] |
姜华, 李文正, 黄士鹏, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组跨重大构造期油气成藏过程与成藏模式. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(5): 11-23. JIANG Hua, LI Wenzheng, HUANG Shipeng, et al. Process and model of hydrocarbon accumulation spanning major tectonic phases of Sinian Dengying Formation in the Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(5): 11-23. |
| [23] |
韩云浩, 姜振学, 张志遥, 等. 含油气盆地超高油气柱形成的有利地质条件. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(2): 125-135. HAN Yunhao, JIANG Zhenxue, ZHANG Zhiyao, et al. Favorable geological conditions for the formation of ultra-high petroleum columns in petroliferous basins. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(2): 125-135. |
| [24] |
关蕴文, 周锋, 蒲仁海, 等. 西湖凹陷平北缓坡带盖层特征及封堵性评价. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(10): 34-41. GUAN Yunwen, ZHOU Feng, PU Renhai, et al. Caprock characteristics and sealing evaluation of Pingbei gentle slope belt in Xihu Sag. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(10): 34-41. |
| [25] |
王宇鹏. 四川安岳大气田泥岩盖层封闭天然气有效性定量评价[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2019. WANG Yupeng. Quantitative evaluation of effectiveness of mudstone caprock sealing natural gas in Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2019. |
| [26] |
DING Xiong, WU Han, SUN Yuefeng, et al. Genetic types of carbonate shoal reservoirs in the Middle Triassic of the Sichuan Basin(SW China). Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 99: 61-74. |
 2024, Vol. 36
2024, Vol. 36