| 2-(2- 苯并咪唑基)-6- 甲基吡啶铜(I)溴化物的合成与发光 |
b. 冶金与化学工程学院, 江西赣州341000
b. School of Metallurgy and Chemical Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China
一价铜配合物由于在太阳能电池、电致发光器件、光学传感器、生物标记及发光探针等领域具有重要的潜在应用而成为近年来科学家们的研究热点[1-4].相对于铼、铱、铂、钌等贵金属,铜具有资源丰富和价格低廉等明显优势,而且一价铜金属配合物也具有上述贵金属配合物的良好发光性能.研究还表明,与一价铜原子配位成键的配体所具有的电子特性和空间几何特征对于所形成的一价铜配合物的发光性质有重要影响[5-13].因而,正确合理地选择与一价铜中心进行配位的配体对控制和修饰一价铜配合物的发光性质至关重要.因此,本文选择具有二齿螯合配位特性的氮杂环螯合配体-2-(2-苯并咪唑基)-6-甲基吡啶(简称Hbmp),应用三苯基膦作为第二辅助配体,与溴化亚铜进行分子组装,合成得到了一固态发光的单核铜(I)溴化物,并对其固态结构特征和光致发光性质进行了研究.
1 实验部分 1.1 主要试剂和仪器溴化亚铜(分析纯)、三苯基膦(分析纯)、丙酮(分析纯)、二氯甲烷(分析纯)、正己烷(分析纯)等均购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司.2-(2-苯并咪唑基)-6-甲基吡啶是根据文献合成方法自行制得[14].美国Perkin-Elme 公司的240C 元素分析仪和LS55 荧光分光光度计; 德国布鲁克AXS 公司的SMART APEX-CCD X 射线单晶衍射仪.
1.2 配合物合成26.5 mg 三苯基膦和7.1 mg 溴化亚铜在二氯甲烷中搅拌反应约3 h, 得到一无色透明溶液,然后往其加入2-(2-苯并咪唑基)-6-甲基吡啶配体10.4 mg, 继续搅拌4 h 后得到一黄色溶液.在旋转蒸发仪上浓缩蒸干得到一黄色固体,用约3 mL 的二氯甲烷和丙酮的混合溶剂(体积比为3∶1) 溶解并转移至20 mL试管中,在其液面上慢慢加入约12 mL 正己烷,几天后在扩散界面部位长出黄色块状晶体.产率为65 %.元素分析的实验值(C31H26BrCuN3P 的计算值,%):C,60.56 (60.54); H,4.28 (4.26); N,6.80 (6.83).
1.3 晶体结构测定大小为0.22 mm × 0.12 mm × 0.08 mm 的单晶在Bruker SMART CCD X 射线单晶衍射仪上进行衍射分析,利用石墨单色化Mo Kα (λ = 0.71073 Å)射线为光源,在293(2) K 温度下收集衍射数据,收集到独立衍射点3580 个,其中I>2σ(I)的可观察衍射点有2664 个,数据经LP 校正.晶体结构通过直接法和差值Fourier 合成解出,运用SHELX-97 程序解析,全矩阵最小二乘法进行修正,所有氢原子理论加入,最后偏离因子R1 = 0.0666,wR2 = 0.1799.配合物1 的晶体结构数据存放于剑桥晶体数据中心(CCDC 872688),可免费直接索取.配合物1 的晶体学参数列于表 1,部分键长和键角数据列于表 2.
| 表1 配合物1 的晶体学参数 |
 |
| 点击放大 |
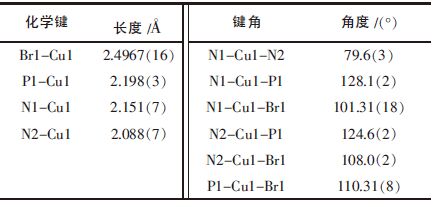
| 表2 配合物1 的部分键长和键角 |
 |
| 点击放大 |
2 结果与讨论 2.1 配合物的制备
配合物1 在制备过程中生成一无色中间产物,该中间产物在空气中非常稳定,而且易溶于二氯甲烷和三氯甲烷,其分子结构已通过X-射线单晶衍射法证实为一双核的铜(I) 配合物,其分子式为[(PPh3)2Cu(μ-Br)2Cu(PPh3)][15].配合物1 的分子结构和合成路线如图 1 所示.
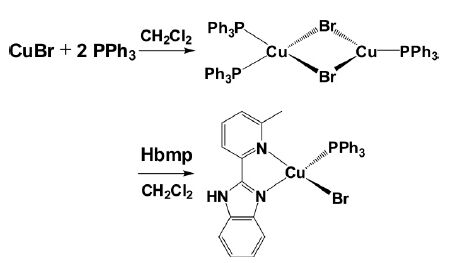 |
| 图 1 配合物1 的分子结构和合成路线 |
2.2 晶体结构
如图 2 所示,配合物1 是一个单核的基于二齿螯合配体2-(2-苯并咪唑基)-6-甲基吡啶的铜(I)溴化铜原子与苯并咪唑基上的sp3-杂化N 原子能形成更为稳定的化学键,这与文献中有关铜(I)配合物的报道相一致[8, 16, 17].同时,也注意到,在配合物1 中,相邻分子的Hbmp 配体之间的间距较短,约为3.27Å和3.45Å,远小于芳香环发生有效π-π 作用的最大间距(3.8Å)[18],这表明相邻的Hbmp 配体间存在弱的π-π 作用,而配合物分子则通过这些弱的π-π 作用发生有效的分子堆叠排列,从而形成如图 3 所示的一维链状结构.
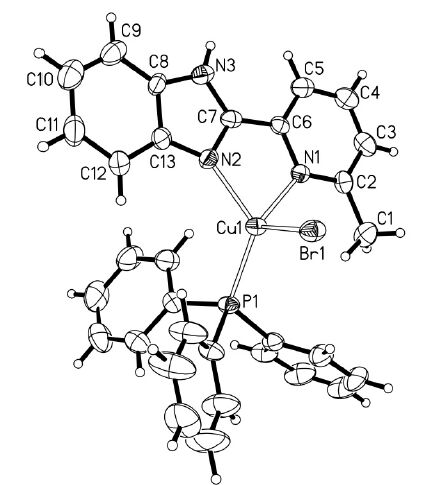 |
| 图 2 配合物1 的晶体结构 |
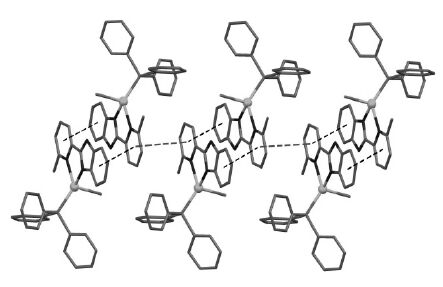 |
| 图 3 配合物1 的分子堆积图 |
2.3 固态发光性质
如图 4 所示,室温下,Hbmp 配体表现出一个λmax为373 nm 的固态紫光发射,它主要是由于Hbmp物, 其中心铜原子Cu1 为四配位, 分别与N1、N2、P1和Br1 相连接,由于Hbmp 配体的锐角螯合配位限制,形成一个畸形四面体构型.Hbmp 配体应用分别来自苯并咪唑基和吡啶基上的两个sp3-杂化N 原子与中心Cu 原子进行螯合配位.研究发现,与吡啶基相连的Cu1-N1 键的长度(2.151(7)Å)稍大于与苯并咪唑基相连的Cu1-N2 键的键长(2.088(7)Å),这表明中心配体内的π→π* 电荷转移(ILCT)跃迁所致.然而,在常温下,配合物1 的固体在λmax=573 nm 位置有一个固态黄绿光发射.比较Hbmp 配体,配合物1 的固态磷光发射可以确认并不是来源于Hbmp 配体内的电荷转移跃迁(ILCT).参考相关文献报道[6, 7, 13-15, 19],配合物1 的最高占据分子轨道(HOMO)主要分布于铜原子和溴原子,可能含有少许三苯基膦的贡献,然而其最低未占分子轨道(LUMO)基本分布在Hbmp 配体上.因此,配合物1 的固态发光可能主要来源于金属到配体(Cu(I)→Hbmp)的电荷转移跃迁(MLCT),但包含一定量的卤素到配体(Br→Hbmp)的电荷转移(XLCT)特征.
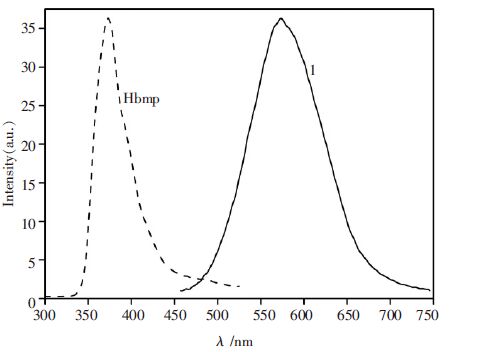 |
| 图 4 配体Hbmp 和配合物1 的固态发射光谱 |
3 结论
选用2-(2- 苯并咪唑基)-6- 甲基吡啶作为二齿螯合配体,合成得到一单核的一价铜溴化物[Cu(Hbmp)(PPh3)Br] (1).配合物1 的中心铜原子采取四配位方式,处于一个由两个氮原子、一个溴原子和一个磷原子所形成的变形四面体中,并通过配体Hbmp 间的π-π 作用发生有序堆叠排列从而形成一维的链状结构.配合物1 表现出一个固态黄绿光发射,主要来源于金属到配体的电荷转移(MLCT)跃迁和卤素到配体的电荷转移(XLCT)跃迁.
| [1] |
Bessho T, Constable E C, Graetzel M, et al. An element of surpriseefficient copper-functionalized dye-sensitized solar cells[J].
Chemical Communications, 2008, 32: 3717–3719. |
| [2] |
Zhang Q, Zhou Q, Cheng Y, et al. Highly efficient green phosphores- cent organic light-emitting diodes based on CuI complexes[J].
Ad- vanced Materials, 2004, 16(5): 432–436. DOI: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095. |
| [3] |
Perruchas S, Goff X F L, Maron S, et al. Mechanochromic and ther- mochromic luminescence of a copper iodide cluster[J].
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(32): 10967–10969. DOI: 10.1021/ja103431d. |
| [4] |
McMillin D C, McNett K M. Photoprocesses of copper complexes that bind to DNA[J].
Chemical Reviews, 1998, 98(3): 1201–1219. DOI: 10.1021/cr9601167. |
| [5] |
Chen L X, Shaw G B, Novozhilova I, et al. MLCT state structure and dynamics of a copper (I) diimine complex characterized by pumpprobe X-ray and laser spectroscopies and DFT calculations[J].
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(23): 7022–7034. DOI: 10.1021/ja0294663. |
| [6] |
Armaroli N, Accorsi G, Cardinali F, et al. Photochemistry and photo- physics of coordination compounds : copper[J].
Topics in Current Chemistry, 2007, 280: 69–115. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-73347-8. |
| [7] |
Ford P C, Cariati E, Bourassa J. Photoluminescence properties of multinuclear copper(I) compounds[J].
Chemical Reviews, 1999, 99(12): 3625–3647. DOI: 10.1021/cr960109i. |
| [8] |
McCormick T, Jia W L, Wang S. Phosphorescent Cu (I) complexes of 2-(2′-pyridylbenzimidazolyl)benzene: impact of phosphine ancillary ligands on electronic and photophysical properties of the Cu (I) complexes[J].
Inorganic Chemistry, 2006, 45(1): 147–155. DOI: 10.1021/ic051412h. |
| [9] |
Cuttell D G, Kuang S M, Fanwick P E, et al. Simple Cu(I) complexes with unprecedented excited-state lifetimes[J].
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(1): 6–7. DOI: 10.1021/ja012247h. |
| [10] |
Smith C S, Branham C W, Marquardt B J, et al. Oxygen gas sensing by luminescence quenching in crystals of Cu (xantphos ) (phen ) + complexes[J].
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(40): 14079–14085. DOI: 10.1021/ja103112m. |
| [11] |
Ryu C K, Vitale M, Ford P C. Photoluminescence properties of the structurally analogous tetranuclear copper(I) clusters Cu4X4(dpmp)4 (X=I, Br, Cl; dpmp=2-(diphenylmethyl)pyridine)[J].
Inorganic Chemistry, 1993, 32(6): 869–874. DOI: 10.1021/ic00058a020. |
| [12] |
Tsuboyama A, Kuge K, Furugori M, et al. Photophysical properties of highly luminescent copper(I) halide complexes chelated with 1,2- bis (diphenylphosphino)benzene[J].
Inorganic Chemistry, 2007, 46(6): 1992–2001. DOI: 10.1021/ic0608086. |
| [13] |
Araki H, Tsuge K, Sasaki Y, et al. Luminescence ranging from red to blue: a series of copper (I) -halide complexes having rhombic {Cu2 (μ-X)2}(X= Br and I) units with N-heteroaromatic ligands[J].
Inorganic Chemistry, 2005, 44(26): 9667–9675. DOI: 10.1021/ic0510359. |
| [14] |
Sun W H, Hao P, Zhang S, et al. Iron(II) and cobalt(II) 2-(benz- imidazolyl) -6 -(1 -(arylimino)ethyl)pyridyl complexes as catalysts for ethylene oligomerization and polymerization[J].
Organometallics, 2007, 26(10): 2720–2734. DOI: 10.1021/om0700819. |
| [15] | 陈景林, 宋鹏, 温和瑞, 等. 双核铜(I)配合物的合成及其固态发光性质的研究[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2010, 1(1): 27–29. |
| [16] |
Min J, Zhang Q, Sun W, et al. Neutral copper (I) phosphorescent compllexes from their ionic counterparts with 2-(2′-quinolyl)benz- imidazole and phosphine mixed ligands[J].
Dalton Transactions, 2011, 40: 686–693. DOI: 10.1039/C0DT01031F. |
| [17] |
Chen J L, Cao X F, Gu W, et al. Phosphorescent copper (I) com- plexes bearing 2-(2-benzimidazolyl)-6-methylpyridine and phos- phine mixed ligands[J].
Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2011, 14(12): 1894–1897. DOI: 10.1016/j.inoche.2011.09.005. |
| [18] |
Hunter C A, Meah M N, Sanders J K M. Dabco-metalloporphyrin binding: ternary complexes, host-guest chemistry and the measure- ment of π-π interactions[J].
Journal of the American Chemical So- ciety, 1990, 112(15): 5773–5780. DOI: 10.1021/ja00171a016. |
| [19] |
Chen J L, Cao X F, Gu W, et al. Luminescent mononuclear copper (I) heteroleptic complexes with 6-cyano-2,2′-bipyridine[J].
Inor- ganic Chemistry Communications, 2012, 15: 65–68. DOI: 10.1016/j.inoche.2011.09.040. |
 2012, Vol. 3
2012, Vol. 3


