2. "油气藏地质及开发工程"国家重点实验室·西南石油大学, 四川 成都 610500
2. State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610500, China
在钻井作业过程中,过平衡条件下液柱压力大于地层压力,钻井液侵入地层,在近井壁地带会形成储层伤害带,从而极大地影响油气藏的产能,尤其在致密砂岩气藏,钻井液有时造成的伤害是致命的、难以恢复的[1-4],为了准确了解钻井液对储层的伤害程度,必须研究钻井液对储层伤害的深度[5-7]。蒋官澄等[8-9]根据实验结果,采用回归的方法建立了侵入深度与时间、孔隙度、渗透率及压差等参数的关系模型。周福建等[10]研究了用钻井液性能参数、储层物性参数、钻井工况参数等资料预测钻井液侵入深度的模型与方法。汪伟英等[11]建立了预测钻井液浓度随井径变化的数学模型,利用钻井液性能、地层孔渗参数及钻井数据确定钻井液的深度。钻井液的侵入会对岩芯的电阻率产生较大的影响[12-13],根据这一特征,可通过测井数据评价钻井液侵入深度[14]。由于实验岩芯稀缺,实验难度较大,关于钻井液侵入深度的实验研究并不多见,尤其针对致密砂岩钻井液侵入的实验研究更是缺乏,实验结果是客观事实的真实反映[6],为此,以东海某储层致密砂岩为研究对象,开展了钻井液侵入深度的实验研究,利用两种方法测试并计算了一定压差条件下钻井液侵入深度,并准确评价钻井液对储层的伤害程度,从而为储层保护提供了可靠依据。
1 实验岩样实验岩样取自XX-2井古近系渐新统花港组下段,其井深为4 604.00~4 613.49 m,地层岩性主要为砂泥岩互层,部分岩样的物性参数见表 1,实验岩样初始含水饱和度采用毛管自吸法建立[15]。
| 表1 实验岩样基础物性 Table 1 Basic physical property of experimental samples |
钻井液滤液侵入岩样后会降低岩样的电阻,增强岩样的导电性,因此,测试钻井液侵入过程中岩样电阻的变化来评价钻井液的伤害深度,成为有效的室内实验评价方法[12-13, 16]。另外,可以通过记录侵入岩芯的钻井液流量来评价钻井液的侵入深度,根据质量守恒定律,通过实验获得钻井液滤液最大侵入量(
| $L_{{\rm{fmax}} } π r^2 \phi \left( {1 - S_{{\rm{wo}}} } \right){\rm{ = }}Q_{\max }$ | (1) |
式中:
r—实验岩样半径,cm;
ϕ—孔隙度,%;
采用MFC-Ⅰ型高温高压多功能水平井伤害评价仪(图 1),记录单位岩样长度电阻和累计侵入量随时间的变化情况,待各监测段电阻不再明显变化时停止实验。实验温度为80 ℃,围压为20 MPa、压差为3.5 MPa。通过监测单位长度岩样电阻(R)和累计侵入量(Q)随侵入时间(t)的变化情况,绘制R-t和Q-t关系曲线。
 |
| 图1 MFC-Ⅰ型高温高压多功能水平井伤害评价仪 Fig. 1 MFC-Ⅰ multifunctional horizontal wells damage evaluation instrument for high temperature and pressure |
图 2为实验得到的R-t曲线。图中,R0、R1、R2、R3分别为岩样上不同的监测位置。由图可知,钻井液滤液侵入岩样的过程中,单位长度岩样的电阻表现为先快速后缓慢降低的过程,这是因为钻井液滤液侵入岩样的过程可分为两个阶段:钻井液滤液快速增大岩样总矿化度和总矿化度缓慢平衡阶段。此外,钻井液滤液侵入单位长度岩样所需时间呈增大趋势,这是因为随着钻井液滤液侵入深度(
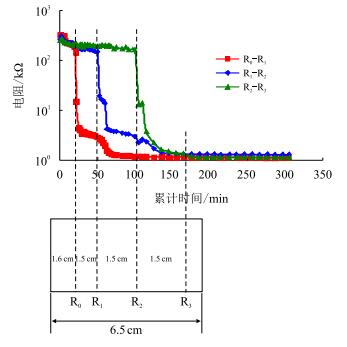 |
| 图2 致密砂岩岩样钻井液侵入R-t曲线 Fig. 2 Tight sandstone samples of drilling fluid invasion R-t curve |
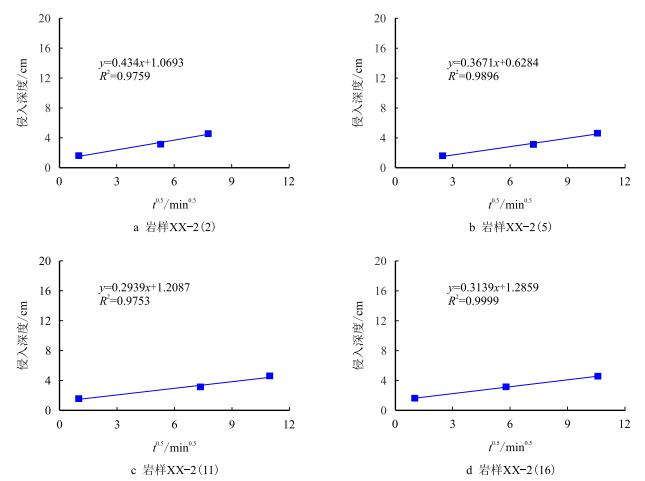
根据实验数据,岩样的R-t曲线和Q-t曲线见图 3和图 4。对图 3和图 4进行数据处理,可以得到
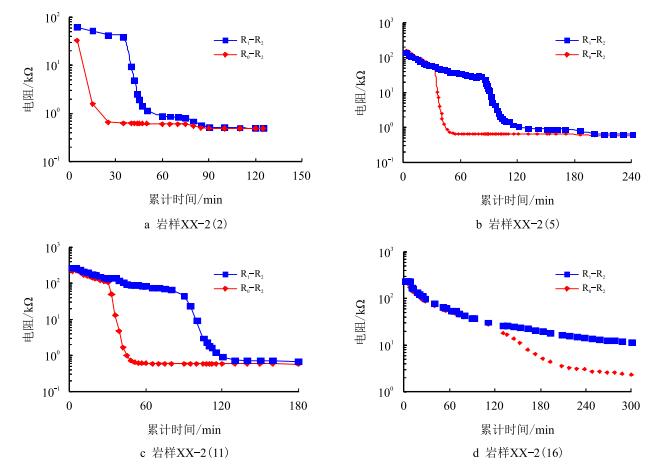 |
| 图3 岩样R-t曲线 Fig. 3 R-t curve of sample |
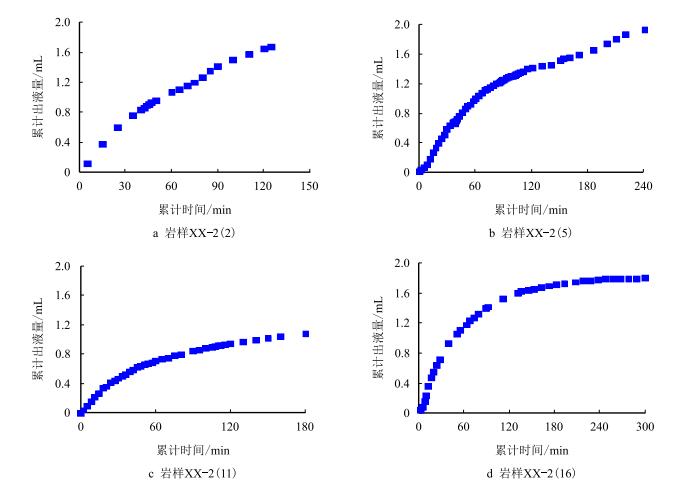 |
| 图4 岩样Q-t曲线 Fig. 4 Q-t curve of sample |
 |
|
图5
岩样 |
 |
|
图6
岩样 |
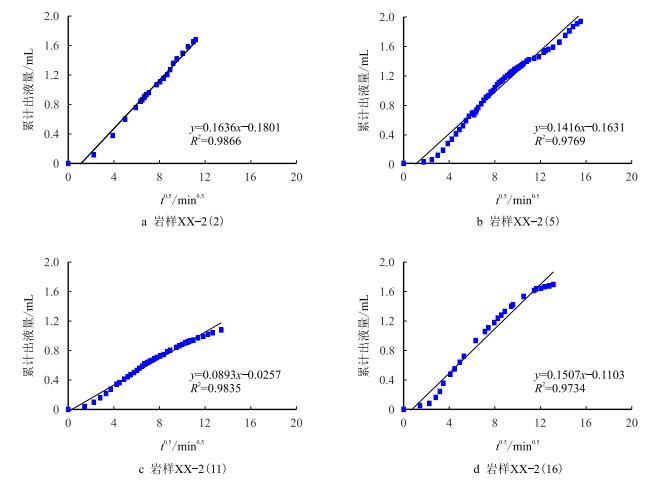
| $L_{\rm{f}} = at^{0.5} + b$ | (2) |
式(2) 中a与b是可由实验数据拟合得出的经验参数,若获得钻井液滤液侵入稳定时间(
| $\dfrac{{Q_{\max }^{'} |_{t_{\max } + 10} - Q_{\max } |_{t_{\max } } }}{{Q_{\max } |_{t_{\max } } }} \leqslant 2\%$ | (3) |
式中:
由式(3) 确定钻井液侵入稳定时间
根据实验结果,拟合得到
| 表2 Q-t0.5曲线拟合结果 Table 2 Results of Q-t0.5 curve fitting |
|
表3 |
通过式(3) 可以确定
| 表4 花港组下段致密砂岩岩样钻井液侵入深度 Table 4 Drilling fluid invasion depth of tight sandstone samples of Huagang Formation lower part |
从表 4可知,电阻测试法计算的花港组下段致密砂岩基块岩样钻井液侵入深度主要分布在34.00~50.00 cm,体积法计算结果为30.00~56.00 cm。可以看出,电阻测试法与体积法测试的结果较为吻合。
对岩芯侵入深度进行测试的同时,采用SCMS-CⅡ型全自动岩芯孔渗测量仪测定钻井液侵入前岩样的渗透率K1,作为基准渗透率,然后测定钻井液侵入后岩样的渗透率K2,利用式(4) 计算出钻井液侵入储层伤害程度,根据钻井液伤害程度评价指标[18](表 5),可以评价钻井液侵入后岩芯伤害程度(表 6)。由表 6可知,钻井液侵入储层后Rs为78.241%~97.877%,钻井液侵入后储层岩芯伤害程度均为强。
| 表5 钻井液侵入储层伤害程度评价表 Table 5 Drilling fluid reservoir damage degree evaluation table |
| 表6 钻井液侵入储层伤害程度 Table 6 Damage of drilling fluid to reservoir |
| $R_{\rm{s}} = \dfrac{{K_1 - K_2 }}{{K_1 }} \times 100\%$ | (4) |
式中:
(1) 电阻测试法与体积法是测取钻井液侵入深度的有效方法,而电阻率法得到的钻井液侵入深度更为准确。
(2) 可以利用钻井液滤液侵入稳定时间来判断钻井液最大侵入量,从而计算出钻井液的最大侵入量。
(3) 电阻测试法计算的花港组下段致密砂岩基块岩样钻井液侵入深度主要在34.00~ 50.00 cm,而体积法计算的钻井液侵入深度结果为30.00~56.00 cm。钻井液侵入损害程度为81.50%~95.60%,平均损害程度为93.62%,钻井液侵入储层的损害程度为强。
(4) 致密砂岩气藏钻井完井液侵入基块较浅,但损害程度严重,在钻井完井作业中控制滤失与加强封堵,在后期作业中要考虑侵入深度及损害程度,选择合理解除措施。
| [1] | 王良. 致密砂岩气藏钻井伤害对产能的影响研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2015. |
| [2] |
李皋, 孟英峰, 唐洪明, 等. 气体钻井高效开发致密砂岩气藏[J].
天然气工业, 2007, 27(7): 59–62.
LI Gao, MENG Yingfeng, TANG Hongming, et al. Gas drilling used for efficient development of tight sandstone gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(7): 59–62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.07.017 |
| [3] |
王滢, 唐洪明, 谢晓永, 等. 致密砂岩气藏水基欠平衡钻井伤害评价[J].
天然气工业, 2008, 28(12): 71–73.
WANG Ying, TANG Hongming, XIE Xiaoyong, et al. Evaluation on the damage degree of water-based underbalanced drilling technology applied in tight sandstone gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(12): 71–73. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.12.020 |
| [4] |
吴志均, 周春梅, 唐红君. 气体钻井应用于致密砂岩气藏开发的思索[J].
钻采工艺, 2009, 32(4): 5–7.
WU Zhijun, ZHOU Chunmei, TANG Hongjun. Discussion on tight sandstone gas reservoir development by gas drilling[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2009, 32(4): 5–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2009.04.002 |
| [5] |
康毅力, 张杜杰, 游利军, 等. 裂缝性致密储层工作液伤害机理及防治方法[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 37(3): 77–84.
KANG Yili, ZHANG Dujie, YOU Lijun, et al. Mechanism and control methods of the working fluid damages in fractured tight reservoirs[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Universtiy (Science & Technology Edition), 2015, 37(3): 77–84. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2015.03.16.04 |
| [6] |
游利军, 康毅力. 油气储层岩石毛细管自吸研究进展[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 31(4): 112–116.
YOU Lijun, KANG Yili. Progress in research on spontaneous capillary imbibition of oil and gas reservoir rocks[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Universtiy (Science & Technology Edition), 2009, 31(4): 112–116. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2009.04.024 |
| [7] |
何琰, 彭军. 隆昌北须二段致密砂岩储层特征及主控因素[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 32(5): 65–69.
HE Yan, PENG Jun. The reservoir characteristics and main control factors of the second member of Xujiahe Formation in north Longchang[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Universtiy (Science & Technology Edition), 2010, 32(5): 65–69. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2010.05.010 |
| [8] | 蒋官澄, 鄢捷年, 吴学诗. 计算钻井液侵入储层深度的数学模型[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 1992, 9(6): 12–19. |
| [9] |
蒋官澄, 鄢捷年, 吴学诗. 计算完井液中固相颗粒侵入储层深度的数学模型[J].
钻井液与完井液, 1995, 12(2): 66–73.
JIANG Guancheng, YAN Jienian, WU Xueshi. Mathematical model for the calculation of invasion depth of solid particles of completion fluid into reservoir[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 1995, 12(2): 66–73. |
| [10] |
周福建, 杨贤友, 刘雨晴, 等. 用现场资料预测钻井液伤害储层深度[J].
钻井液与完井液, 2000, 17(4): 8–10.
ZHOU Fujian, YANG Xianyou, LIU Yuqing, et al. Prediction of formation damage depth with field data[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2000, 17(4): 8–10. doi: 10.-3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2000.04.003 |
| [11] | 汪伟英, 胡荣, 高振龙. 确定钻井液侵入油层伤害的数值模拟计算方法[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 2002, 19(5): 10–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2002.05.003 |
| [12] |
王敏, 李万才, 冯雪, 等. 钻井液侵入对储层电阻率影响方式的数值模拟与实验研究[J].
测井技术, 2015, 39(3): 272–276.
WANG Min, LI Wancai, FENG Xue, et al. On drilling fluid invasion influence on resistivity logging characteristics by numerical modeling and experimental method[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2015, 39(3): 272–276. |
| [13] |
胡国恒, 姚永君, 胡在凯, 等. 钻井液侵入对储层电性物性影响实验研究[J].
测井技术, 1999, 23(5): 323–326, 333.
HU Guoheng, YAO Yongjun, HU Zaikai, et al. An experiment on the effect of drilling fluid invasion on reservoir electrical and petrophysical properties[J]. Well Logging Technology, 1999, 23(5): 323–326, 333. doi: 10.3969/j.-issn.1004-1338.1999.05.001 |
| [14] |
范翔宇, 龚明, 夏宏泉, 等. 裂缝性致密砂岩储层钻井液侵入深度的定量计算方法[J].
天然气工业, 2012, 32(6): 60–64.
FAN Xiangyu, GONG Ming, XIA Hongquan, et al. A quantitative calculation method of the invasion depth of drilling fluids into the fractured tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012, 32(6): 60–64. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2012.06.015 |
| [15] |
游利军, 康毅力, 陈一健. 致密砂岩含水饱和度建立新方法毛管自吸法[J].
西南石油学院学报, 2005, 27(1): 28–31.
YOU Lijun, KANG Yili, CHEN Yijian. New method of water saturation of tight gas spontanoeus imbibition[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2005, 27(1): 28–31. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2005.01.008 |
| [16] |
潘和平, 樊政军, 马勇. 电阻率测井的钻井液侵入校正方法[J].
天然气工业, 2005, 25(7): 41–43.
PAN Heping, FAN Zhengjun, MA Yong. Correction method of drilling fluid invasion of resistivity logging[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(7): 41–43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:-1000-0976.2005.07.014 |
| [17] |
王建华, 鄢捷年, 郑曼, 等. 钻井液固相和滤液侵入储层深度的预测模型[J].
石油学报, 2009, 30(6): 923–926.
WANG Jianhua, YAN Jienian, ZHENG Man, et al. Prediction model for invasion radius of solids and filtrate in drilling fluids[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 923–926. doi: 10.7623/syxb200906023 |
| [18] | 徐同台, 熊友明, 康毅力, 等. 保护油气层技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010. |
 2017, Vol. 39
2017, Vol. 39


