奶牛乳腺炎是由于奶牛乳腺组织受到物理或化学损伤,致病微生物入侵等因素影响而发生的炎症反应;患病奶牛的乳汁中体细胞数增多,并常有致病菌残留,最终导致牛奶品质下降[1],且患病奶牛常遭过早淘汰,从而给养殖户带来巨大的经济损失。更重要的是,一旦摄入致病菌残留奶,人类的健康将会受到威胁。MicroRNA(miRNA)是一类长度18~24个核苷酸的非编码RNA,在转录后水平通过与靶基因结合从而发挥调控作用。大量的研究表明,bta-miR-223在发生奶牛乳腺炎后,其表达量出现明显上调趋势。
Pu等[2]构建了无乳链球菌诱导的乳腺炎奶牛miRNA的表达谱,发现bta-miR-223表达增加约3倍。Lawless等[3]发现,乳房链球菌感染奶牛乳腺组织36 h后,乳汁中单核细胞bta-miR-223表达量上调了2.44倍。Sun等[4]发现,bta-miR-223在金黄色葡萄球菌感染前的牛乳外泌体中并不存在,而感染后出现上调表达。另有研究者通过注射金黄色葡萄球菌悬液到健康牛的乳腺组织构建乳腺炎动物模型,采集健康牛和金葡菌乳腺炎奶牛的乳腺组织,经测序分析发现bta-miR-223表达量分别上调了约4.89倍[5]、5.16倍[6]、6.36倍[7]。
乳腺炎患病奶牛中bta-miR-223的表达量明显高于健康奶牛,那么极可能是某些抗炎基因或参与缓解炎症反应的相关信号通路的基因表达被bta-miR-223抑制。但由于靶基因预测分析结果体量庞大,并且其涉及的信号通路众多,使得研究者花费大量时间和精力去挖掘各个靶基因和信号通路之间的联系。所以,本研究利用生物信息学分析技术,对bta-miR-223的候选靶基因进行蛋白质互作关系分析,绘制调控网络,以期为bta-miR-223参与奶牛乳腺炎抗性调控机制的研究提供参考。
1 材料与方法使用Targetscan(http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/)和miRWalk(http://mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/)进行bta-miR-223靶基因预测。使用STRING(https://string-db.org/)功能性蛋白质互作网络在线分析软件,对候选靶基因进行蛋白质互作分析。使用Cytoscape(https://cytoscape.org/)可视化工具进行bta-miR-223的互作候选靶基因重点参与的KEGG通路网络绘制。
2 结果通过miRWalk在线预测,获得了bta-miR-223的4 157个候选靶基因;通过Targetscan在线预测,获得了bta-miR-233的365个候选靶基因。106个候选靶基因在两个预测结果中重叠出现。在预测得到的106个候选靶基因中,与其他蛋白质存在较多互作关系的基因包括:CBLB、FBXW7、SMURF2、FGFR2、UBA2、RAB10、HSP90B1等。并且,他们参与了抗原加工过程中的泛素化和蛋白酶体降解,免疫应答,翻译后蛋白质修饰,先天免疫系统和中性粒细胞脱颗粒等反应途径。
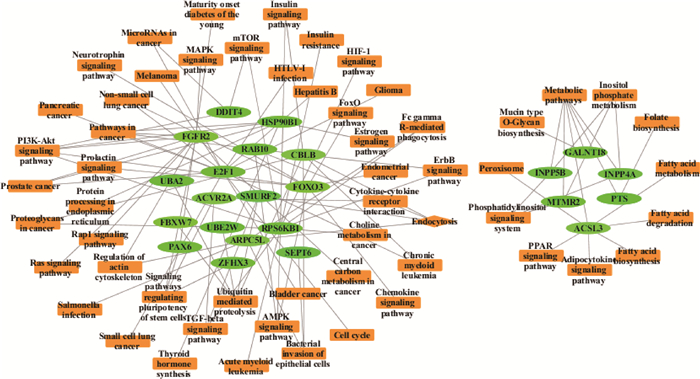
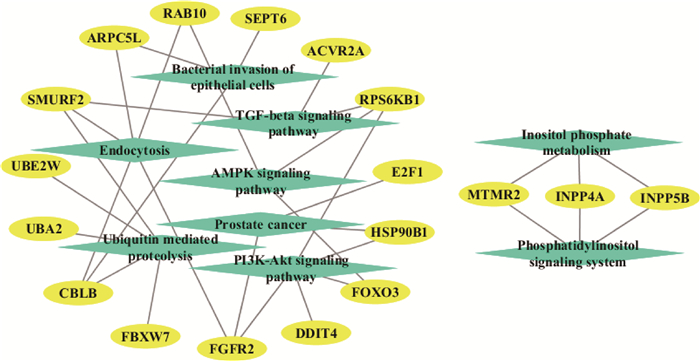
在两个独立的调控网络中,主网络中PI3K-Akt、上皮细胞的细菌入侵等是候选靶基因主要参与的信号通路,次网络中靶基因主要参与代谢信号通路(图 1)。将KEGG通路富集分析结果可视化,发现这些候选靶基因显著富集在上皮细胞的细菌入侵、胞吞作用以及PI3K-Akt、TGF-β、AMPK等信号通路(图 2)。
|
椭圆代表基因,长方形代表信号通路 Ellipses represent genes and rectangles represent signal pathways 图 1 Bta-miR-223候选靶基因调控网络分析 Fig. 1 Analysis of regulatory network of bta-miR-223 candidate target genes |
|
椭圆代表基因,菱形代表信号通路 Ellipses represent genes and diamonds represent signaling pathways 图 2 Bta-miR-223候选靶基因KEGG通路富集分析结果 Fig. 2 KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of bta-miR-223 candidate target genes |
在bta-miR-223候选靶基因显著富集的信号通路中,上皮细胞对细菌入侵防御和胞吞作用是奶牛乳腺组织抵抗细菌入侵和感染的必要程序。巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞等具有吞噬功能的细胞,分布在组织和血液中,可以消灭入侵的细菌。此外,研究表明激活PI3K/Akt信号通路可以抑制氧化应激和促炎反应[8],它还在姜黄素对LPS激活的小胶质细胞的抗炎作用中起关键作用[9]。研究者发现,抑制PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路可促进关节软骨细胞的自噬,减轻骨关节炎大鼠的炎症反应[10],抑制PI3K/Akt/eNOS途径可以减轻人冠状动脉内皮细胞损伤和炎症反应[11]。
Bta-miR-223的候选靶基因中,FBXO30是F-box蛋白家族成员,是主要在细胞质中表达的一种可溶性蛋白[12]。研究者报道FBXO30基因敲除的小鼠,由于乳房发育不良,雌性不能培育它们的后代,并指出FBXO30与双极纺锤体驱动蛋白EG5相互作用是乳房发育中的关键点[13]。FBXW7基因所编码的蛋白属于F-box蛋白家族的一员。作为一种细胞周期调节和肿瘤抑制因子,胃肠道间质瘤中FBXW7的表达下调,可以促进细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移[14]。UBA2是泛素样调节剂激活酶2。研究表明,UBA2在A549细胞(腺癌人类肺泡基底上皮细胞)中的敲除,可以显著抑制癌细胞增殖和并促进癌细胞凋亡[15]。
综上表明,bta-miR-223可能通过调控FBXO30、SMURF2、FBXW7、UBA2等,进而参与抗原加工、先天免疫系统和中性粒细胞脱颗粒反应,以及上皮细胞的细菌入侵、胞吞作用、PI3K-Akt等信号通路发挥重要调控作用。这些发现将有力支持bta-miR-223参与细菌型奶牛乳腺炎抗性调控机制的探索。
4 结论Bta-miR-223候选靶基因FBXO30与SMURF2,FBXW7与UBA2等存在蛋白互作关系。候选靶基因参与上皮细胞的细菌入侵、胞吞作用以及PI3K-Akt、TGF-β、AMPK等信号通路,可能通过参与抗原加工、先天免疫系统和中性粒细胞脱颗粒反应,以及上皮细胞的细菌入侵、胞吞作用、PI3K-Akt等信号通路发挥重要作用。
| [1] |
肖锋. 奶牛乳腺炎的病因、临床表现和防治措施[J]. 现代畜牧科技, 2019(3): 112–113.
XIAO F. Causes, clinical manifestations and preventive measures of cow mastitis[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2019(3): 112–113. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | PU J H, LI R, ZHANG C L, et al. Expression profiles of miRNAs from bovine mammary glands in response to Streptococcus agalactiae-induced mastitis[J]. J Dairy Res, 2017, 84(3): 300–308. DOI: 10.1017/S0022029917000437 |
| [3] | LAWLESS N, REINHARDT T A, BRYAN K, et al. microRNA regulation of bovine monocyte inflammatory and metabolic networks in an in vivo infection model[J]. G3 (Bethesda), 2014, 4(6): 957–971. DOI: 10.1534/g3.113.009936 |
| [4] | SUN J J, ASWATH K, SCHROEDER S G, et al. microRNA expression profiles of bovine milk exosomes in response to Staphylococcus aureus infection[J]. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16: 806. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2044-9 |
| [5] | LI R, ZHANG C L, LIAO X X, et al. Transcriptome microRNA profiling of bovine mammary glands infected with Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16(3): 4997–5013. |
| [6] | CAI M C, HE H B, JIA X B, et al. Genome-wide microRNA profiling of bovine milk-derived exosomes infected with Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2018, 23(4): 663–672. DOI: 10.1007/s12192-018-0876-3 |
| [7] | LUORENG Z M, WANG X P, MEI C G, et al. Comparison of microRNA profiles between bovine mammary glands infected with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14(1): 87–99. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.22498 |
| [8] | YANG X G, HUO F Q, LIU B, et al. Crocin inhibits oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory response of microglial cells associated with diabetic retinopathy through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2017, 61(4): 581–589. DOI: 10.1007/s12031-017-0899-8 |
| [9] | CIANCIULLI A, CALVELLO R, PORRO C, et al. PI3k/Akt signalling pathway plays a crucial role in the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in LPS-activated microglia[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2016, 36: 282–290. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.05.007 |
| [10] | XUE J F, SHI Z M, ZOU J, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 89: 1252–1261. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.130 |
| [11] | LI J B, WANG H Y, YAO Y, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-138 alleviates human coronary artery endothelial cell injury and inflammatory response by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2017, 21(8): 1482–1491. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13074 |
| [12] |
李忠花, 张小慧, 李桂源. F-Box蛋白家族新成员FBXO30基因的融合表达[J]. 湖南医科大学学报, 2001, 26(6): 495–498.
LI Z H, ZHANG X H, LI G Y. Study on the fusion expression of FBXO30: a novel member of F-box protein family[J]. Bulletin of Hunan Medical University, 2001, 26(6): 495–498. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | LIU Y, WANG Y, DU Z W, et al. Fbxo30 regulates mammopoiesis by targeting the bipolar mitotic Kinesin Eg5[J]. Cell Rep, 2016, 15(5): 1111–1122. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.083 |
| [14] | KOGA Y, IWATSUKI M, YAMASHITA K, et al. The role of FBXW7, a cell-cycle regulator, as a predictive marker of recurrence of gastrointestinal stromal tumors[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2019. DOI: 10.1007/s10120-019-00950-y |
| [15] | JIANG B Y, FAN X X, ZHANG D, et al. Identifying UBA2 as a proliferation and cell cycle regulator in lung cancer A549 cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(8): 12752–12761. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.28543 |



