2. 青藏高原动物遗传资源保护与利用教育部和四川省重点实验室, 成都 610041;
3. 成都惠泰生物医药有限公司, 成都 610041;
4. 西南民族大学校医院, 成都 610041
2. Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education and Sichuan Province for Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Animal Genetic Resource Reservation and Utilization, Chengdu 610041, China;
3. Chengdu Huitai Biomedicine CO., LTD., Chengdu 610041, China;
4. Hospital of Southwest Minzu University, Chengdu 610041, China
同源异型框基因表达转录因子对动物的细胞分化和胚胎发育过程有重要作用[1]。矮小同源盒基因(short stature homeobox 2, Shox2),又称SHOX2、SHOT、OG12,是高度保守的同源异型框基因转录因子的一种,与骨骼、神经、心等多个系统的器官组织的发育密切相关[2-4]。最新研究发现,Shox2基因对肺的生命活动也有重要影响,其高度甲基化与肺癌具有密切关系,可能成为肺癌的早期筛查指标[5-6]。但目前,国内外有关Shox2基因研究的物种主要是在人和鼠上,关于家兔Shox2基因的研究尚未见报道。
本研究旨在通过克隆新西兰白兔Shox2基因,预测其编码蛋白的结构与功能,并用RT-qPCR技术确定其在不同发育阶段各组织的表达谱和表达规律,从而为今后深入研究家兔Shox2基因的结构和功能提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料分别采集E20.5 d(E表示embryo,即胚胎中期)、E28.5 d(即胚胎后期)、出生后10 d(即幼龄期)、A(A表示adult,即成年期)4个不同时期新西兰白兔的肾、心、大血管、真皮、大脑、肺、脾、胆囊、肝、肌肉组织,置于液氮中保存备用,每个时期3只动物,共12只。
1.2 主要试剂PrimeSTAR® Max DNA Polymerase DNA高保真聚合酶、逆转录试剂盒、Premix TaqTM、pMD19-T Vector、D2000 DNA Marker、SYBGreenⅡ、T4 DNA连接酶、限制性内切酶BamH I和EcoR I、RNAiso Reagent均购自大连宝生物工程有限公司(TaKaRa);DNA凝胶回收试剂盒、质粒小量提取试剂盒均购自美国Axygen公司;pET-32a(+)质粒载体、DNA marker、大肠杆菌DH5α、BL21感受态细胞均购自北京天根生化科技有限公司(Tiangen)。
1.3 Shox2基因克隆和RT-qPCR使用的引物根据GenBank中的Shox2的基因序列,利用软件Primer5.0设计引物,并在5′和3′端分别引入酶切位点(下划线序列为引入的酶切位点,加粗部分为保护性碱基),引物由上海生工生物工程股份有限公司(上海,中国)合成。引物序列及扩增片段信息见表 1。
|
|
表 1 本研究使用的引物序列 Table 1 The primer sequences used in this study |
取家兔胚胎和成年肾、心、肝各50 mg剪碎后加入RNAiso Reagent提取总RNA,使用BioSpec-nano分光光度计和琼脂糖凝胶电泳法测定RNA的浓度和纯度,按RT Reagents试剂盒说明书合成cDNA,-20 ℃保存。
1.5 家兔Shox2基因的克隆和测序以cDNA为模板进行PCR反应,扩增家兔Shox2基因全长CDS区,反应体系:Ex TaqTM Version 2.0 plus dye 12.5 μL,ddH2O 8.5 μL,上下游引物各1 μL,cDNA 2 μL。PCR反应条件:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性40 s,56 ℃退火40 s,72 ℃延伸60 s,35个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min,4 ℃保存。PCR产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定,电泳使用100 V,80 mA,30 min。将获得的目的片段与pMD19-T Vector质粒载体在16 ℃金属浴中连接1 h,构建重组质粒。总反应体系体积为10 μL,连接产物转化至大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,用氨苄青霉素抗性固体培养基进行蓝白斑筛选和菌落PCR验证,测序阳性菌落。
1.6 家兔Shox2蛋白质的生物信息学分析使用DNAMAN对家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列与人、鼠兔、小鼠的Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列进行同源性比对。使用PBIL-IBCP网站的在线软件Network Protein SequenceAnalysis(http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/secpred_gor4.pl)分析家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列的二级结构;家兔Shox2蛋白的三级结构使用在线工具SWISS-MODEL(http://swissmodel.expasy.org/)进行分析;使用Protparamg在线软件(http://au.expasy.org/tools/protparam.html)分析家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸的理化性质。通过网站在线软件BCEPRED(http://crdd.osdd.net/raghava/bcepred/bcepred_submission.html)预测分析Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列的B细胞抗原表位。通过MEGA5.2软件对家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列进行同源性比对分析,建立系统进化树。
1.7 融合蛋白TrxA-Shox2的诱导表达和Western blot验证将鉴定阳性的PMD19-T-质粒和pET32a(+)质粒分别经过BamHⅠ和XholⅠ限制性内切酶双酶切后进行连接形成pET32a(+)-Shox2重组质粒,转化进入BL21(DE3)细胞。优化培养IPTG浓度、时间、温度,取表达的蛋白20 μg进行SDS-PAGE,随后进行Western blot验证,一抗(Santa Cruz,sc-81955)稀释500倍,二抗(Santa Cruz,sc-516102)稀释5 000倍。
1.8 家兔Shox2基因的时空表达特征分析经过多种内参基因之间的比较,最终确定以GAPDH为内参基因[7],分析家兔Shox2在胚胎中期(E20.5 d)、胚胎后期(E28.5 d)、幼龄期(出生后10 d)、成年期(A)4个阶段各器官的表达规律。RT-qPCR反应使用20 μL反应体系:SYBR Green Ⅱ10 μL,上下游引物各0.4 μL,ddH2O 7.2 μL,cDNA 2 μL。RT-qPCR反应条件:95 ℃ 3 min;95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 30 s,循环数为40个。熔解曲线为55~95 ℃每15 s增加0.5 ℃。
1.9 数据处理RT-qPCR结果采用2-ΔΔCt法进行分析,数据用“x±SD”表示,利用SPSS19.0软件T-test进行差异显著性分析,P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
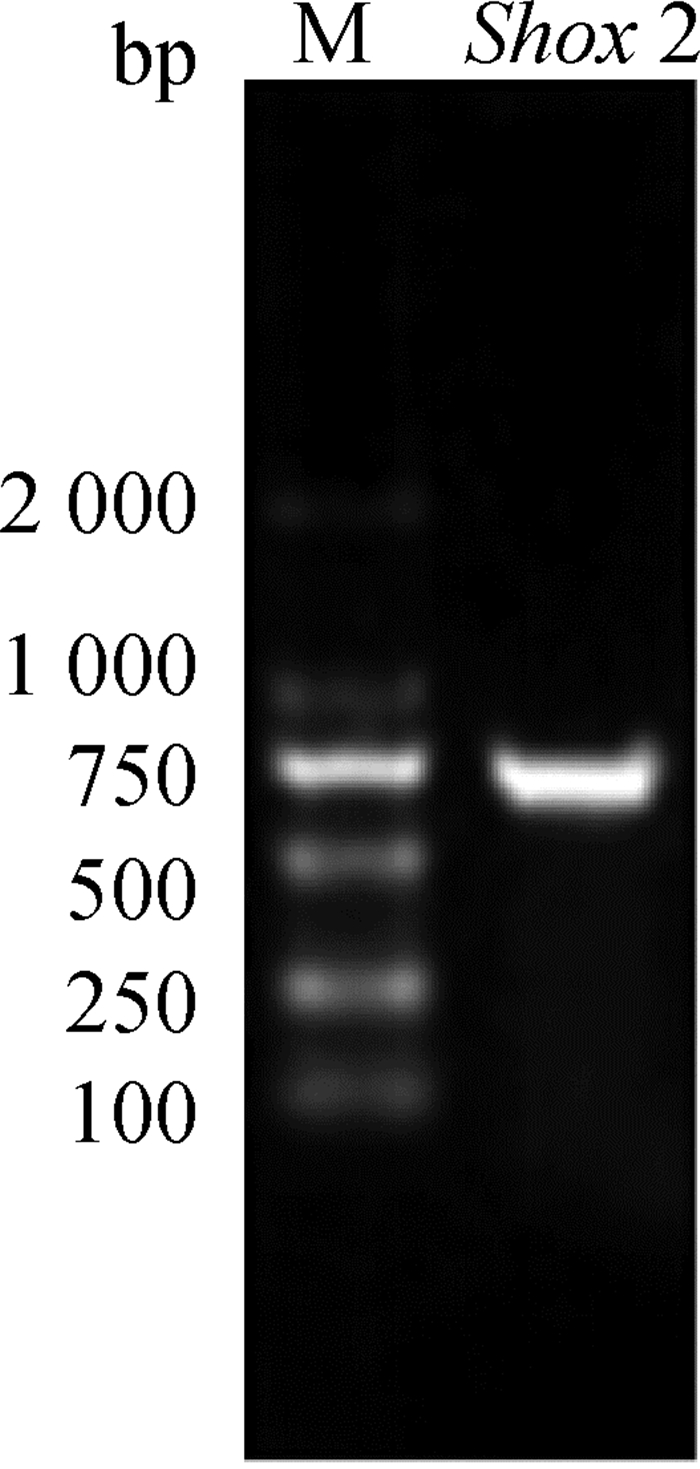
2 结果 2.1 家兔Shox2基因的克隆以获得的cDNA为模板,F1、R1为上下游引物,进行PCR反应,对PCR产物进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,结果如图 1所示。
|
图 1 Shox2扩增产物琼脂糖凝胶电泳结果 Figure 1 Agarose gel electrophoresis result of amplified product of Shox2 |
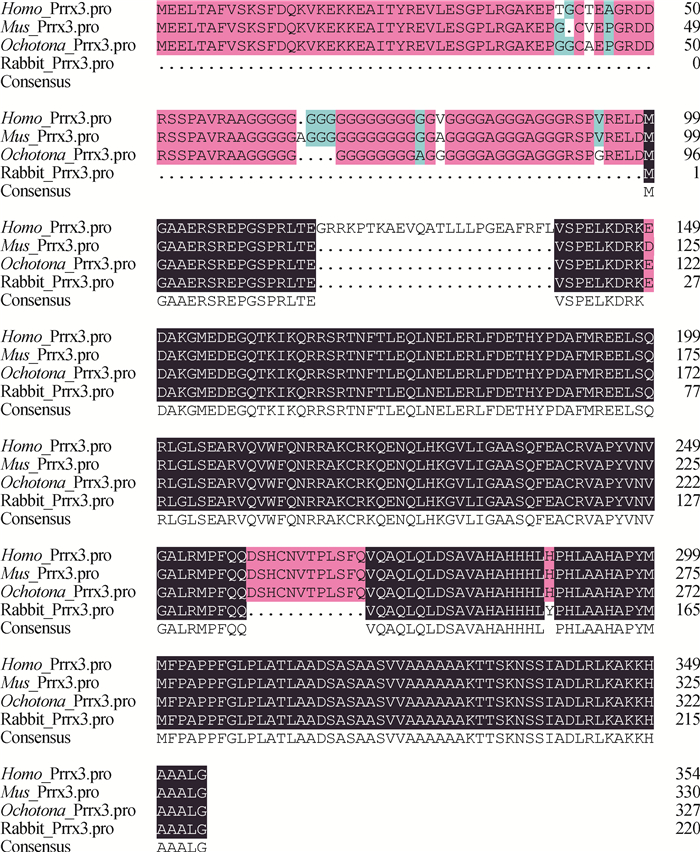
经核酸测序验证,成功克隆得到Shox2基因(登录号:KP726285),与预测序列XM_008266391.1相比第463位核苷酸由C变成了T,但是并不引起编码氨基酸种类的改变。将得到的家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列与人、小鼠和鼠兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列进行同源性对比,结果见图 2。由图 2可知,与人、小鼠Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列相比,家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列有相似的N端,而C端较短,各物种C端局部有较高的特异性。Shox2蛋白的功能域位于C端,N端未见明显活性。
|
图中不同颜色表示同源基因编码的相同和不同氨基酸所在位置 The different colors in the figure indicate the locations of the same and different amino acids encoded by homologous genes 图 2 人、小鼠、鼠兔、家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列的同源性对比 Figure 2 Comparison of amino acid sequences of Shox2 protein among Oryctolagus cuniculus, Homo sapiens, Mus musculus and Ochotona |
通过多种软件分析Shox2的理化性质、抗原表位、遗传信息学等特征,结果表明,Shox2基因CDS区全长666 bp,编码221个氨基酸。氨基酸含负电荷残基为24个,正电荷残基为30个,蛋白质带正电荷。Shox2蛋白不稳定系数为52.35,为不稳定蛋白。Shox2多肽链的分子式为C1068H1712N324O316S8,分子量24.4 ku,理论等电点为9.42,N端为Met,C端为Leu。
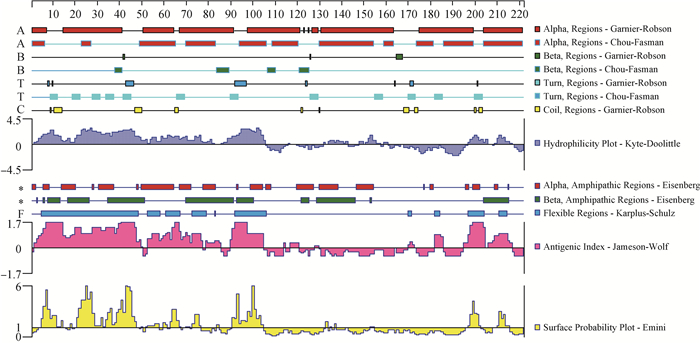
如图 3所示,Shox2蛋白亲水性残基所占比例大于疏水性残基,因此其编码蛋白整体表现为亲水性。分子柔韧性分析结果表明,抗原表位区域分布相对均匀,这些区域活性大、易变形,抗体的识别和结合区域可能是抗原表位的富集区。用BCEPRED软件预测可知,Shox2蛋白4个最可能具有抗原表位的区域分别为1~10 aa、18~47 aa、87~101 aa、192~203 aa。序列上含有较多的β折叠区域、α螺旋区域以及转角,结构较为复杂,在第8~61位氨基酸的同源异型框结构域为典型的螺旋-转角-螺旋模式序列,它可以通过识别特定序列将螺旋插入DNA大沟,氨基末端插入到相邻的小沟从而结合DNA,调节下游基因的表达,从而实现对DNA的转录调控。
|
图中Alpha, Beta, Turn and Coil regions对应的方框的大小和位置为不同算法预测的多肽的各种二级结构的大小和位置;Hydrophilicity plot为亲疏水性分析,正值部分为亲水性,负值为疏水性;Flexible regions为柔韧性区域,表示多肽在此处的抗原决定簇的量较多,因此是可能的免疫靶点。Antigenic index为抗原性指数,为综合考虑蛋白质的活动性、构象、结构、侧链等多种性质后的抗原性的量化分析法,值越大表示越有可能为抗原表位。Surface probability plot为表面可能性 The sizes and positions of the corresponding boxes of Alpha, Beta, Turn and Coil regions in the figure are the sizes and positions of various secondary structures of polypeptides predicted by different algorithms; the Hydrophilicity plot is a hydrophilic and hydrophobic analysis, and the positive values are hydrophilic, the negative values are hydrophobic; the Flexible region is a flexible region, indicating that the polypeptide has more antigenic determinants here, and thus is a possible immunological target. Antigenic index is an antigenicity index, which is a quantitative analysis of antigenicity considering various activities such as activity, conformation, structure and side chain of a protein, a larger value indicates that the antigenic epitope is more likely to be presented. Surface probability plot is the surface possibility 图 3 家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列亲水性及柔韧性的预测 Figure 3 Analysis of hydrophilicity and flexibility of amino acids sequence of Shox2 protein in Oryctolagus cuniculus |
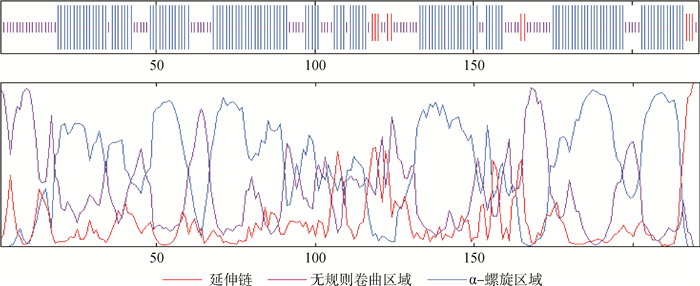
如图 4所示,Shox2蛋白的二级结构通过在线软件Network Protein Sequence Analysis分析得出,Shox2蛋白组成包括3种二级结构:即α-螺旋区域占137个氨基酸,比例为61.99%;无规则卷曲区域占74个氨基酸,比例为33.48%;延伸链占10个氨基酸,比例为4.52%。
|
图 4 家兔Shox2蛋白的二级结构预测 Figure 4 Secondary structure prediction of Shox2 protein in Oryctolagus cuniculus |
对Shox2蛋白质第40~105位氨基酸的三级结构进行预测,结果如图 5所示,符合率为58.97%。

|
图 5 家兔Shox2蛋白的三级结构预测 Figure 5 Tertiary structure prediction of Shox2 protein in Oryctolagus cuniculus |
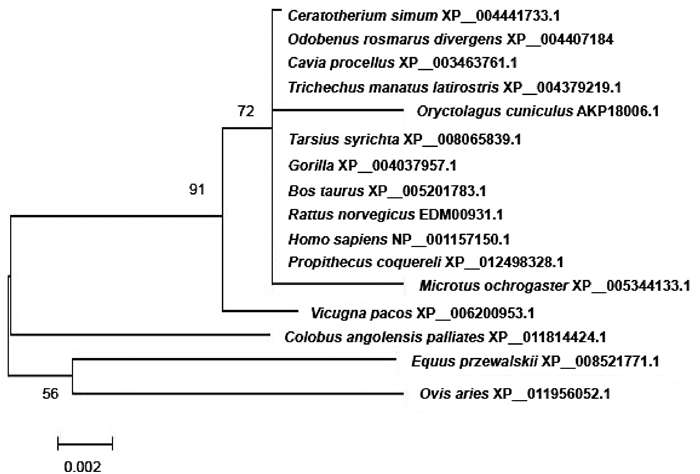
使用MEGA5.2软件对家兔、疣猴、野马、绵羊、眼镜猴、猩猩、褐家鼠、人等16个物种的Shox2蛋白质氨基酸序列的同源性进行对比,并建立系统进化树。本研究选择氨基酸序列而非基因序列是因为氨基酸序列变化更能代表基因进化的本质。结果如图 6所示,家兔Shox2蛋白质氨基酸序列与疣猴、野马、绵羊的同源性较低,与眼镜猴、猩猩、褐家鼠、人的氨基酸序列同源性较高,表明Shox2基因序列在进化中相对保守。
|
图 6 Shox2蛋白质氨基酸序列的系统进化树分析 Figure 6 Phylogenetic tree analyses of amino acid sequence of Shox2 protein |
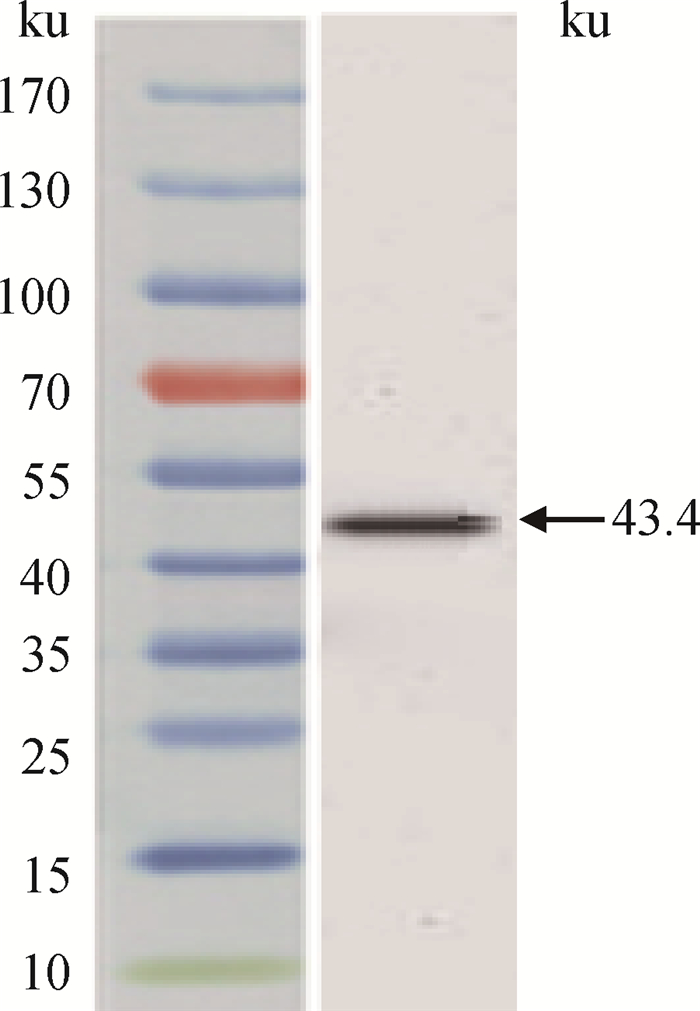
重组质粒pET32(a)-Shox2能够表达融合蛋白TrxA-Shox2。优化BL21表达条件,结果表明,37 ℃下IPTG浓度为1.0 mmol·L-1时诱导过夜可以获得最大的表达量。按一般方法进行融合蛋白亲和纯化、SDS-PAGE和Western blot检测,ECL法显色,PVDF膜在底物液中浸泡1 min,在成像系统VersaDoc 2000下自动曝光显色。融合蛋白大小约为43.4 ku,其中TrxA约19 ku,Shox2约24.4 ku,结果见图 7。
|
图 7 TrxA-Shox2重组蛋白的Western blot检测 Figure 7 Western blot detection result of recombinant protein TrxA-Shox2 |
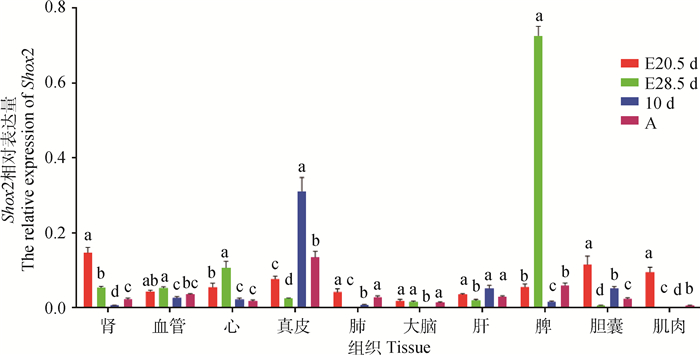
Shox2基因主要在外胚层和中胚层发育成的很多器官中表达,且不同发育阶段多种组织间表达差异显著,见图 8、图 9,纵坐标表示Shox2的相对表达量。在E20.5 d的家兔胚胎组织中,Shox2基因在肾、肌肉和胆囊的表达量高,在脑组织表达量较低;E28.5 d时其在脾和心的表达量较高,在肺和肌肉的表达量较低;10 d时在真皮和肝中表达量较高,在脑和肺表达量较低;成年时,在真皮和脾中的表达量较高,在肌肉表达量较低。
|
相同字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05);不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下图同 The same letter indicates the difference is not significant(P>0.05); The different letters indicate the difference is significant(P < 0.05). The same as the following figure 图 8 家兔Shox2基因mRNA在各器官中不同发育阶段的表达量 Figure 8 Expression analysis of Shox2 mRNA in different tissues at different developmental phases in Oryctolagus cuniculus |

|
图 9 Shox2基因mRNA在各时期不同器官中的表达量变化比较 Figure 9 Expression analysis of Shox2 mRNA at different developmental stages of various tissues in Oryctolagus cuniculus |
Shox2与OG12基因表达的蛋白序列具有99%同源性,有可能是相同的基因[2-3]。Shox2的同源异性框的氨基酸序列与啮齿动物的Phox2同源域最相近,其C端由14个氨基酸残基组成的区域在少数的几种蛋白中是保守的,包括Shox2、Prrx1、Prrx2、Otp和Phox2。在已知的非脊椎动物基因中,这种结构仅存在于果蝇的无芒蛋白中,因此这种结构被称为“无芒结构域”,主要在颅面部、眼、脑中高表达[8]。这种无芒结构域保守的氨基酸序列显示这个区域可能有分子间反应的位点。
人的Shox2基因位于人3号染色体(3q25-26.1),包含6个外显子,编码转录调节因子,有至少2种变异剪接体,即SHOX2a(993 bp)和SHOX2b(570 bp)。其中,SHOX2b的N端只含有6个氨基酸残基,中间为同源域,C端缺少12个氨基酸残基。Shox2基因表达于胚胎期的中胚层和外胚层,与骨、软骨、大脑、神经、脊髓、心等器官的发育,甚至颅面部的形成有关[9]。Shox2基因缺失可能会引起Léri-Weill综合征[10]、Lange综合征[11]、Turnerz综合征等骨骼发育异常疾病。Lange综合征的症状主要是上颌骨裂和唇腭裂[12-14]。在胚胎期,Shox2主要影响近端肢体发育[12]。有研究表明,条件性敲除小鼠Shox2基因,发育中的软骨细胞会过早成熟、增厚,从而导致四肢近端骨较短(例如肱骨、股骨),但不影响肢体远端发育[15-16]。Shox2的直接靶标是Bmp4基因,但Bmp4蛋白可以外源性补充[17]。Shox2在近端肢体表达,而Hoxa13和Hoxd13则调控远端肢体发育[18]。Shox2缺失时骨骼附属结构的发育也会出现异常,因此Shox2也影响骨骼附属结构的发育[19]。此外,Shox2还影响颞颌关节和牙胚的发育,与其他各种影响牙胚发育的调控基因表达方式相似(如Bmp4、FCF8、MSX1、PAX9)[20-22]。Shox2在心发育的早期阶段发挥作用[23-24],特异性地在静脉窦区域表达。敲除Shox2基因可以导致胚胎心发育缺陷,包括窦房结发育缺陷[24-26]。Shox2参与脂肪分布和脂肪库的发育[27-28],其在皮下、肾周围和腹腔内肠系膜周围的表达依次减少。Shox2基因影响肺的生命活动,Shox2-/-胚胎肺部发育极性颠倒,肺末梢出现多个类似于支气管、细支气管样结构,而非成熟的、功能性的大肺泡。Shox2基因的高甲基化与肺癌等多种癌症的关系密切,可以作为多种癌症的早期筛查指标[5-6],许多诊断和检测的方法正在进一步的研究中[28-34]。
本研究结果表明,中晚期胚胎心组织中Shox2基因相较于出生后有较高的表达(P < 0.05),与Hoffmann等[23]的研究结果相似。比较胚胎阶段和出生后的表达量可以认为,Shox2基因对脾、胆囊、肌肉和肾等多种组织的胚胎发育过程尤为重要。
4 结论本研究克隆得到了家兔Shox2基因序列(登录号:KP726285),预测了其结构和功能。Western blot验证了融合蛋白TrxA-Shox2的表达。家兔Shox2蛋白氨基酸序列与眼镜猴、猩猩、褐家鼠、人的氨基酸序列同源性较高。本研究发现,Shox2基因主要在中胚层和外胚层发育成的很多器官都有表达。不同组织和不同时期表达量的变化可能与Shox2基因功能高度相关,并受到严格的调控。
| [1] | KRUMLAUF R, HOLLAND P W, MCVEY J H, et al. Developmental and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse homeobox gene, Hox 2.1[J]. Development, 1987, 99(4): 603–617. |
| [2] | VAN SCHAICK H S A, SMIDT M P, ROVESCALLI A C, et al. Homeobox gene Prx3 expression in rodent brain and extraneural tissues[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1997, 94(24): 12993–12998. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.12993 |
| [3] | SEMAAN A, VAN ELLEN A, MELLER S, et al. SEPT9 and SHOX2 DNA methylation status and its utility in the diagnosis of colonic adenomas and colorectal adenocarcinomas[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2016, 8: 100. DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0267-5 |
| [4] | ROVESCALLI A C, ASOH S, NIRENBERG M. Cloning and characterization of four murine homeobox genes[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1996, 93(20): 10691–10696. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.20.10691 |
| [5] | REN M, WANG C, SHENG D, et al. Methylation analysis of SHOX2 and RASSF1A in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for early lung cancer diagnosis[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2017, 27: 57–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.01.007 |
| [6] | SCHNEIDER K U, DIETRICH D, FLEISCHHACKER M, et al. Correlation of SHOX2 gene amplification and DNA methylation in lung cancer tumors[J]. BMC Cancer, 2011, 11: 102. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-102 |
| [7] |
陈瑞, 杨晓农, 曾婉秋, 等. 家兔不同发育阶段和组织中内参基因的稳定性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2016, 47(3): 447–483.
CHEN R, YANG X N, ZENG W Q, et al. Expression stability analysis of reference genes in different development periods and tissues in oryctolagus cuniculus[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2016, 47(3): 447–483. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | CHESTERMAN E S, GAINEY G D, VARN A C, et al. Investigation of Prx1 protein expression provides evidence for conservation of cardiac-specific posttranscriptional regulation in vertebrates[J]. Dev Dyn, 2001, 222(3): 459–470. |
| [9] | SMITH T M, LOZANOFF S, IYYANAR P P, et al. Molecular signaling along the anterior-posterior axis of early palate development[J]. Front Physiol, 2013, 3: 488. |
| [10] | CENSANI M, ANYANE-YEBOA K, WAPNER R, et al. Rare inheritance of Leri-Weill Syndrome due to crossover of short stature Homeobox Gene (SHOX) deletions between X and Y Chromosomes:a case report[J]. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol, 2013(1): 11. |
| [11] | GROSSCHEDL R, GIESE K, PAGEL J. HMG domain proteins:architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures[J]. Trends Genet, 1994, 10(3): 94–100. DOI: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1 |
| [12] | YU L, GU S P, ALAPPAT S, et al. Shox2-deficient mice exhibit a rare type of incomplete clefting of the secondary palate[J]. Development, 2005, 132(19): 4397–4406. DOI: 10.1242/dev.02013 |
| [13] | HILLIARD S A, YU L, GU S P, et al. Regional regulation of palatal growth and patterning along the anterior-posterior axis in mice[J]. J Anat, 2005, 207(5): 655–667. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00474.x |
| [14] | LI Q, DING J X. Gene expression analysis reveals that formation of the mouse anterior secondary palate involves recruitment of cells from the posterior side[J]. Int J Dev Biol, 2007, 51(2): 167–172. DOI: 10.1387/ijdb.062212ql |
| [15] | COBB J, DIERICH A, HUSS-GARCIA Y, et al. A mouse model for human short-stature syndromes identifies Shox2 as an upstream regulator of Runx2 during long-bone development[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2006, 103(12): 4511–4515. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510544103 |
| [16] | BOBICK B E, COBB J. Shox2 regulates progression through chondrogenesis in the mouse proximal limb[J]. J Cell Sci, 2012, 125: 6071–6083. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.111997 |
| [17] | PUSKARIC S, SCHMITTECKERT S, MORI A D, et al. Shox2 mediates Tbx5 activity by regulating Bmp4 in the pacemaker region of the developing heart[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2010, 19(23): 4625–4633. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq393 |
| [18] | NEUFELD S J, WANG F, COBB J. Genetic interactions between Shox2 and Hox genes during the regional growth and development of the mouse limb[J]. Genetics, 2014, 198(3): 1117–1126. DOI: 10.1534/genetics.114.167460 |
| [19] | VICKERMAN L, NEUFELD S, COBB J. Shox2 function couples neural, muscular and skeletal development in the proximal forelimb[J]. Dev Biol, 2011, 350(2): 323–336. DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.11.031 |
| [20] | YE W D, SONG Y N, HUANG Z, et al. A unique stylopod patterning mechanism by Shox2-controlled osteogenesis[J]. Development, 2016, 143(14): 2548–2660. DOI: 10.1242/dev.138750 |
| [21] | GU S P, WEI N, YU L, et al. Shox2-deficiency leads to dysplasia and ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint in mice[J]. Mech Dev, 2008, 125(8): 729–742. DOI: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.04.003 |
| [22] | LIN D H, HUANG Y D, HE F L, et al. Expression survey of genes critical for tooth development in the human embryonic tooth germ[J]. Dev Dyn, 2007, 236(5): 1307–1312. DOI: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0177 |
| [23] | HOFFMANN S, BERGER I M, GLASER A, et al. Islet1 is a direct transcriptional target of the homeodomain transcription factor Shox2 and rescues the Shox2-mediated bradycardia[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2013, 108(2): 339. |
| [24] | HU W Y, XIN Y G, ZHAO Y N, et al. Shox2:The role in differentiation and development of Cardiac conduction system[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 2018, 244(3): 177–186. DOI: 10.1620/tjem.244.177 |
| [25] | BLASCHKE R J, HAHURIJ N D, KUIJPER S, et al. Targeted mutation reveals essential functions of the homeodomain transcription factor Shox2 in sinoatrial and pacemaking development[J]. Circulation, 2007, 115(14): 1830–1838. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.637819 |
| [26] | LIU H B, CHEN C H, YE W D, et al. Phosphorylation of Shox2 is required for its function to control sinoatrial node formation[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2014, 3(3): e000796. |
| [27] | YAMAMOTO Y J, GESTA S, LEE K Y, et al. Adipose depots possess unique developmental gene signatures[J]. Obesity, 2010, 18(5): 872–878. DOI: 10.1038/oby.2009.512 |
| [28] | WEISS G, SCHLEGEL A, KOTTWITZ D, et al. Validation of the SHOX2/PTGER4 DNA methylation marker panel for plasma-based discrimination between patients with malignant and nonmalignant lung disease[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2017, 12(1): 77–84. |
| [29] | BERGHEIM J, SEMAAN A, GEVENSLEBEN H, et al. Potential of quantitative SEPT9 and SHOX2 methylation in plasmatic circulating cell-free DNA as auxiliary staging parameter in colorectal cancer:a prospective observational cohort study[J]. Br J Cancer, 2018, 118(9): 1217–1228. DOI: 10.1038/s41416-018-0035-8 |
| [30] | ZHANG C Z, YU W J, WANG L, et al. DNA methylation analysis of the SHOX2 and RASSF1A panel in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for lung cancer diagnosis[J]. J Cancer, 2017, 8(17): 3585–3591. DOI: 10.7150/jca.21368 |
| [31] | NI S M, YE M, HUANG T. Short stature homeobox 2 methylation as a potential noninvasive biomarker in bronchial aspirates for lung cancer diagnosis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(37): 61253–61263. |
| [32] | BRANCHI V, SCHAEFER P, SEMAAN A, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of SHOX2 and SEPT9 is a potential biomarker for minimally invasive diagnosis in adenocarcinomas of the biliary tract[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2016, 8: 133. DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0299-x |
| [33] | ZHANG Y A, ZHOU Y, LUO X, et al. SHOX2 is a potent independent biomarker to predict survival of WHO Grade Ⅱ-Ⅲ diffuse gliomas[J]. EBioMedicine, 2016, 13: 80–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.040 |
| [34] | JUNG M, PUTZER S, GEVENSLEBEN H, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of SHOX2 and SEPT9 DNA methylation and cytology in benign, paramalignant, and malignant ascites[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2016, 8: 24. DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0192-7 |



